Figure 6.
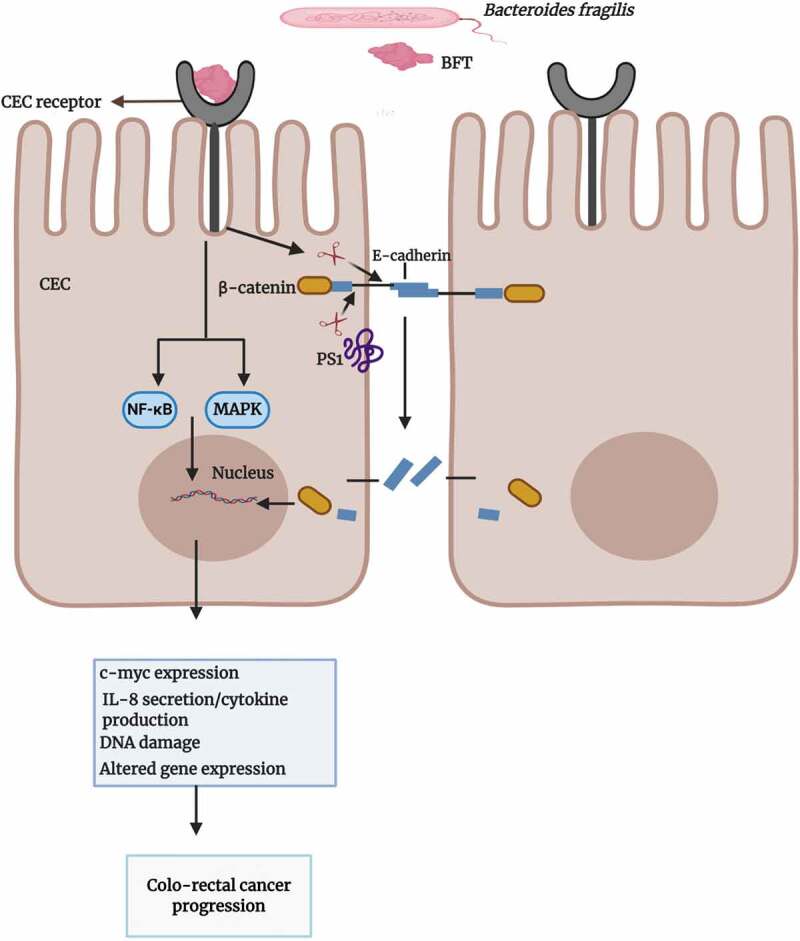
Overview of the potential role of BFT in colo-rectal cancer
The interaction of the Bacteroides fragilis toxin (BFT) and the colonic epithelial cell (CEC) receptor results in E-cadherin cleavage which initiates a cascade of signaling events involving nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and β-catenin. Consequent cellular events of the signals include the proliferation of proinflammatory cytokines (such as IL-8) that promote proinflammatory microenvironments, expression of the proto-oncogene, c-myc, and damage to DNA. Overall, the cellular events triggered by BFT result in CEC proliferation, mucosal inflammation, and potential metastasis.
