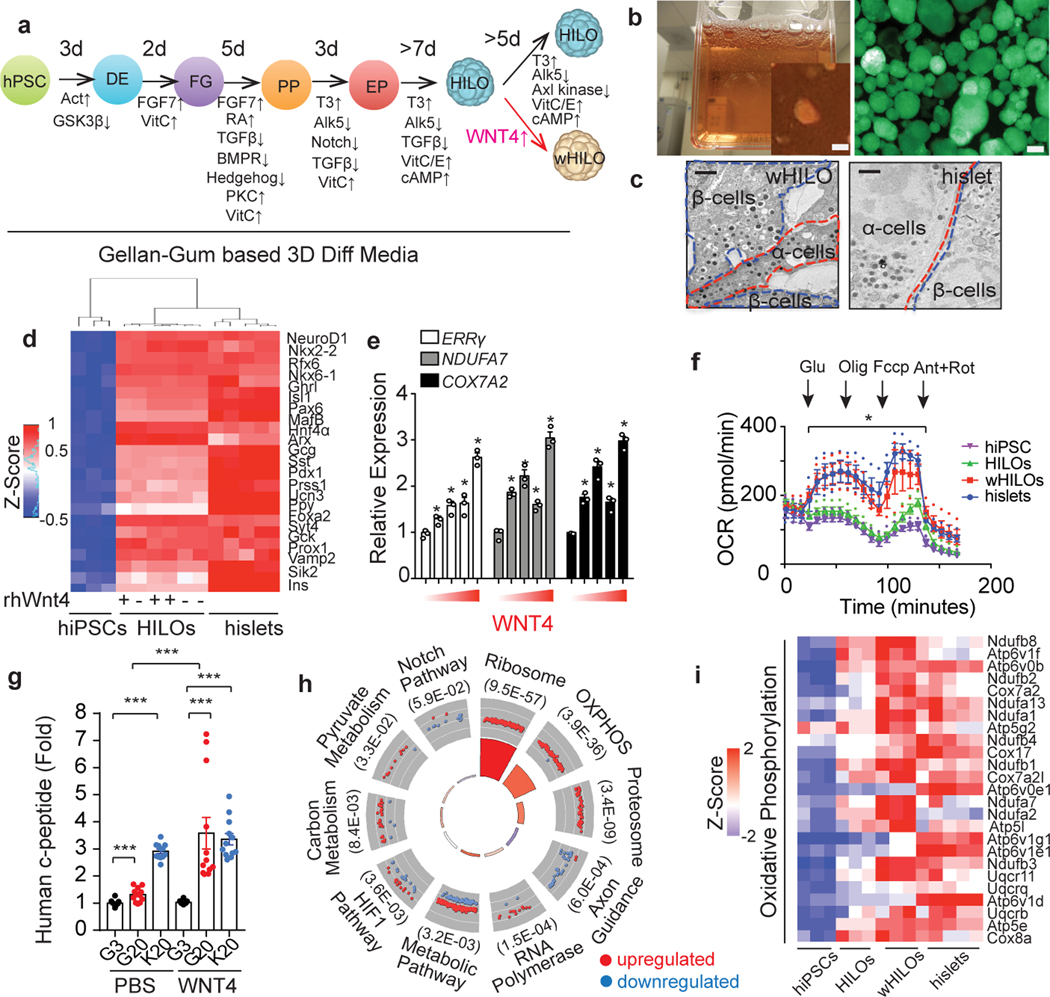
Fig. 1. WNT4 induces functional maturation of human islet-like organoids (HILOs).
a, Schematic of human islet-like organoid (HILO) generation. b, Representative images of HILOs in 3D culture (left panel), and insulin expression (human insulin promoter driven GFP, right panel, scale bar 100 μm). c, Electron microscopy images showing insulin and glucagon granules in β and α cells, respectively, in WNT4-treated HILOs (wHILOs) and human islets. Scale bar, 1 μm. d, Heatmap of relative expressions of key islet genes in hiPSCs (n=3), HILOs treated with PBS (−)(n=3) or WNT4 (+) (n=3), and human islets (n=5) (log2 expression with Z-score). e, Relative expression of ERRγ, NDUFA7 and COX7A2 in HILOs after treatment with increasing concentrations of WNT4 (0, 10, 25, 50, 200ng/ml for 5 days) (n=3). f, Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) measured in hiPSC spheroids (day 0, purple), PBS-treated HILOs (green), WNT4-treated HILOs (red) and human islets (blue) (n=3) g, in vitro human c-peptide secretion in response to 3mM (G3) or 20 mM (G20) glucose or 20mM KCl (K20) from HILOs generated with and without WNT4 treatment (n=12) h, Gene ontology of WNT4-regulated genes in HILOs (100ng/ml WNT4 from day 26 to day 33). i, Heatmap of relative expressions of oxidative phosphorylation genes in 3D cultured hiPSCs (n=3), HILOs (n=3), HILOs after WNT4 treatment (wHILOs) (n=3), and human islets (n=5)(Z-Score). Error bars represent ± SEM.*p<0.05, ***p<0.001, one-tailed, student’s paired t test. Data representative of 3 independent experiments (c, e, f, g).