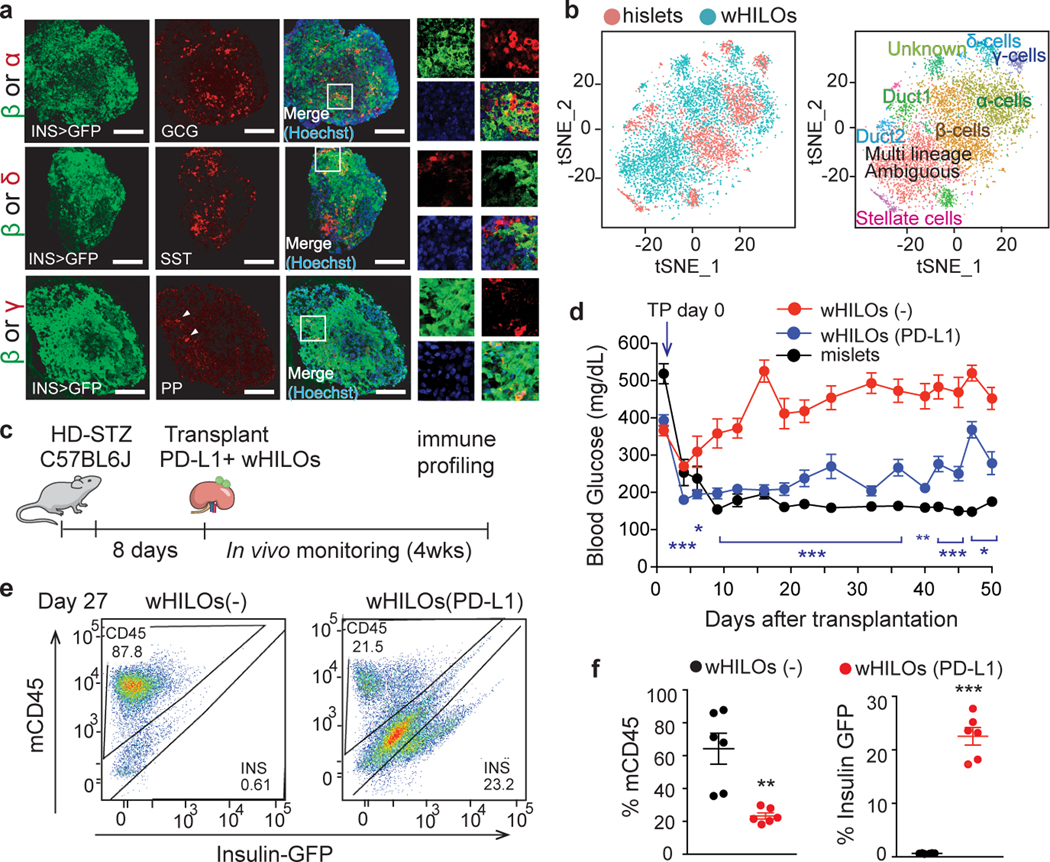
Fig. 2. Exogenous PD-L1 expression extends wHILO functionality in immune competent mice.
a, Representative immunofluorescence staining for glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) in wHILOs. b, tSNE clustering of combined wHILO (blue dots, n=4840) and human islet (red dots, n= 3245) single cell transcriptomes (left panel) and clustering analysis-defined cell types (left). c, Schematic of experimental program. High dose streptozotocin (HD-STZ, 180mg/kg) induced diabetic C57BL6J mice received transplants of wHILOs with and without PD-L1 overexpression (n=500), or mouse islets. d, Random fed blood glucose levels after transplantation of wHILOs with or without PD-L1 expression (n=11 and 9, respectively), and C57BL6J islets (n=7). e, Flow cytometric analysis of insulin-expressing and mouse immune (CD45+) cells recovered from kidney capsule grafts 27 days after transplantation of wHILOs with and without PD-L1 expression (n=6). f, Quantification of analyses in (d). Error bars represent ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, one-tailed, student’s paired t test. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments. Data were representative (e), or compiled from 3 independent samples (b) or experiments (d, f).