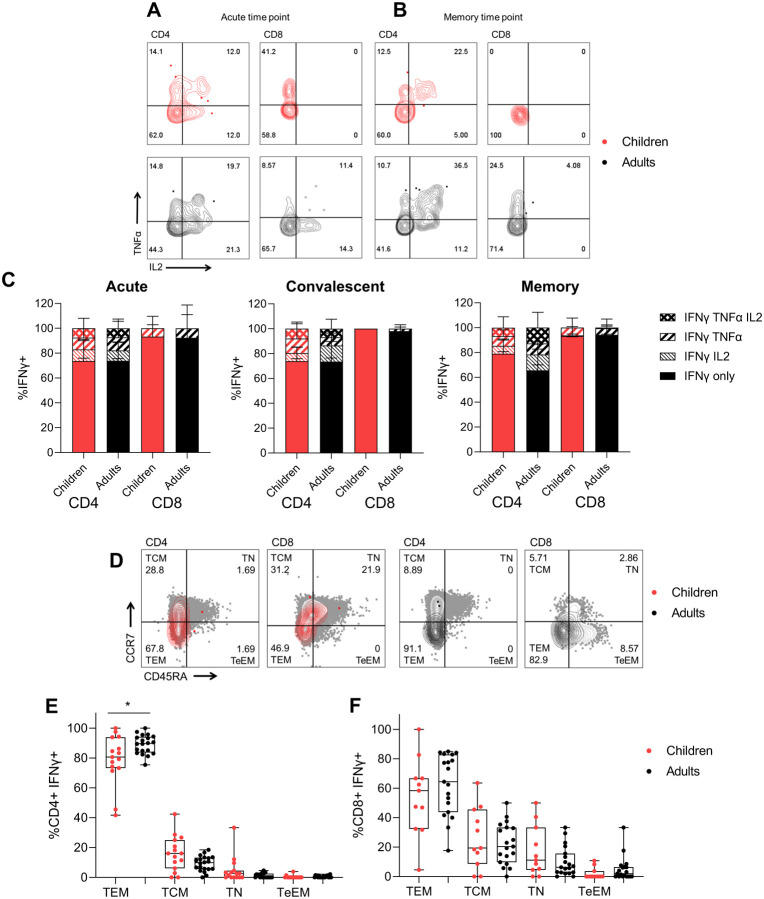
Figure 3 – Cytokine polyfunctional quality is comparable in COVID-19 children and adults, whilst T effector memory phenotype is increased in adults.
Representative FACS plots of TNFα and IL2 producing IFNγ+ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of children (red) and adults (black) at acute (d<14) (A) and memory (child: 118 days, adult: 94 days) (B) time points. (C) The proportion of IFNγ producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells which are single, double or triple cytokine producers at acute (<14 days), convalescent (15–60 days) or memory (61–180 days) time points post symptom onset. Kruskal Wallis test for multiple comparisons was carried out to compare each group between children and adults. (D) Representative FACS plots showing memory phenotypes of IFNγ+ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells based on expression of CCR7 and CD45RA. Sections are T effector memory (TEM), central memory (TCM), terminal effector memory (TeEM) or naïve (TN). Memory phenotype responses in IFNγ+ CD4+ (E) and CD8+ (F) T cells of responders at later time points (15–180 days post symptom onset). Comparisons between children (n=15) and adults (n=20) in each group was performed using Mann-Whitney test, *p<0.05.