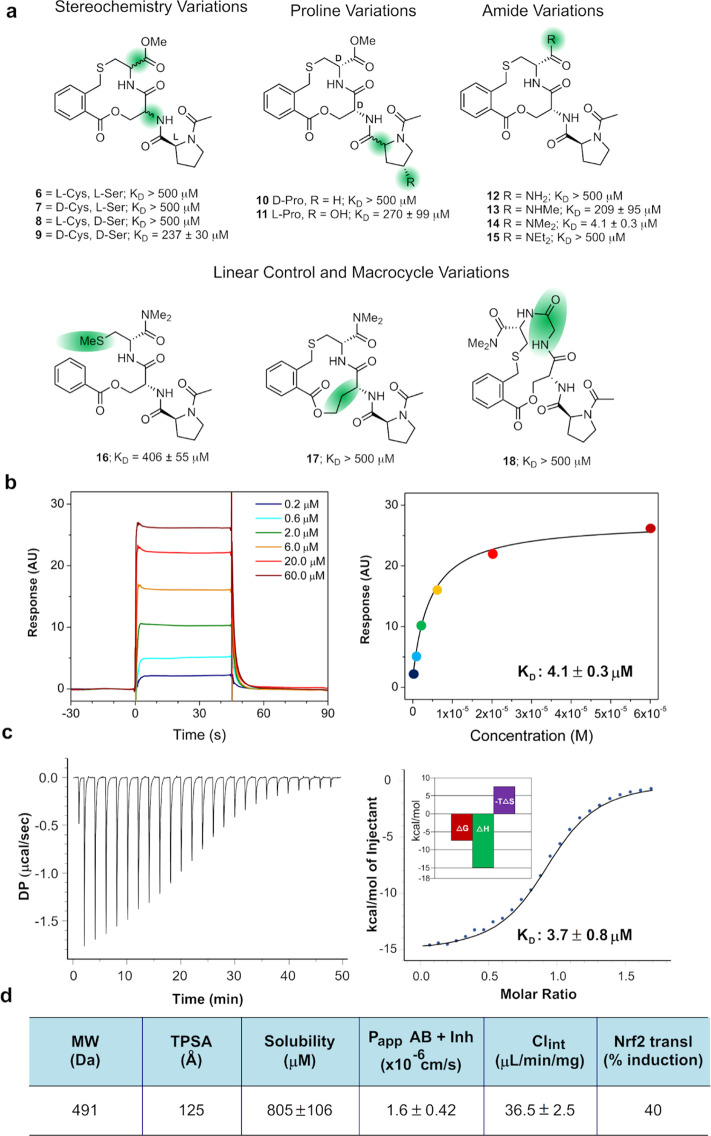
Figure 2.
Characterization of cyclothialidine analogues. (a) Synthesized analogues of the cyclothialidine core that were evaluated as inhibitors of binding of Keap1 to an immobilized peptide derived from Nrf2 by surface plasmon resonance using an inhibition in solution assay (ISA) format. Dissociation constants, reported as mean values ± standard deviation, from three measurements on three distinct samples are given for each analogue. (b) Interaction kinetic analysis of a dilution series of macrocycle 14 in a direct binding assay using immobilized Keap1 (left). Determination of the dissociation constant (KD) for 14 by fitting of the data to a two-parametric sigmoidal equation (right). The dissociation constant was obtained from three measurements on three distinct samples and is reported as the mean value ± standard deviation. (c) Determination of KD for the binding of 14 to Keap1 by isothermal titration calorimetry. The raw heat signals from the exothermic binding reaction (left) have been integrated to yield a binding isotherm (right) from which the thermodynamic parameters were extracted (insert). The dissociation constant was obtained from three measurements on three distinct samples and is reported as the mean value ± standard deviation. (d) Characterization of macrocycle 14 by calculated descriptors (MW and TPSA), solubility in phosphate-buffered saline at 25 °C and pH 7.4, efflux-inhibited permeability across a Caco-2 cell monolayer (Papp AB + inh), human microsomal metabolism (Clint), and induction of Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus (Nrf2 transl) at 256 μM. The values for solubility, cell permeability, and human microsomal metabolism are mean values ± standard deviation from three measurements on three distinct samples. The Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus is the mean from two measurements on two distinct samples.