Figure 4.
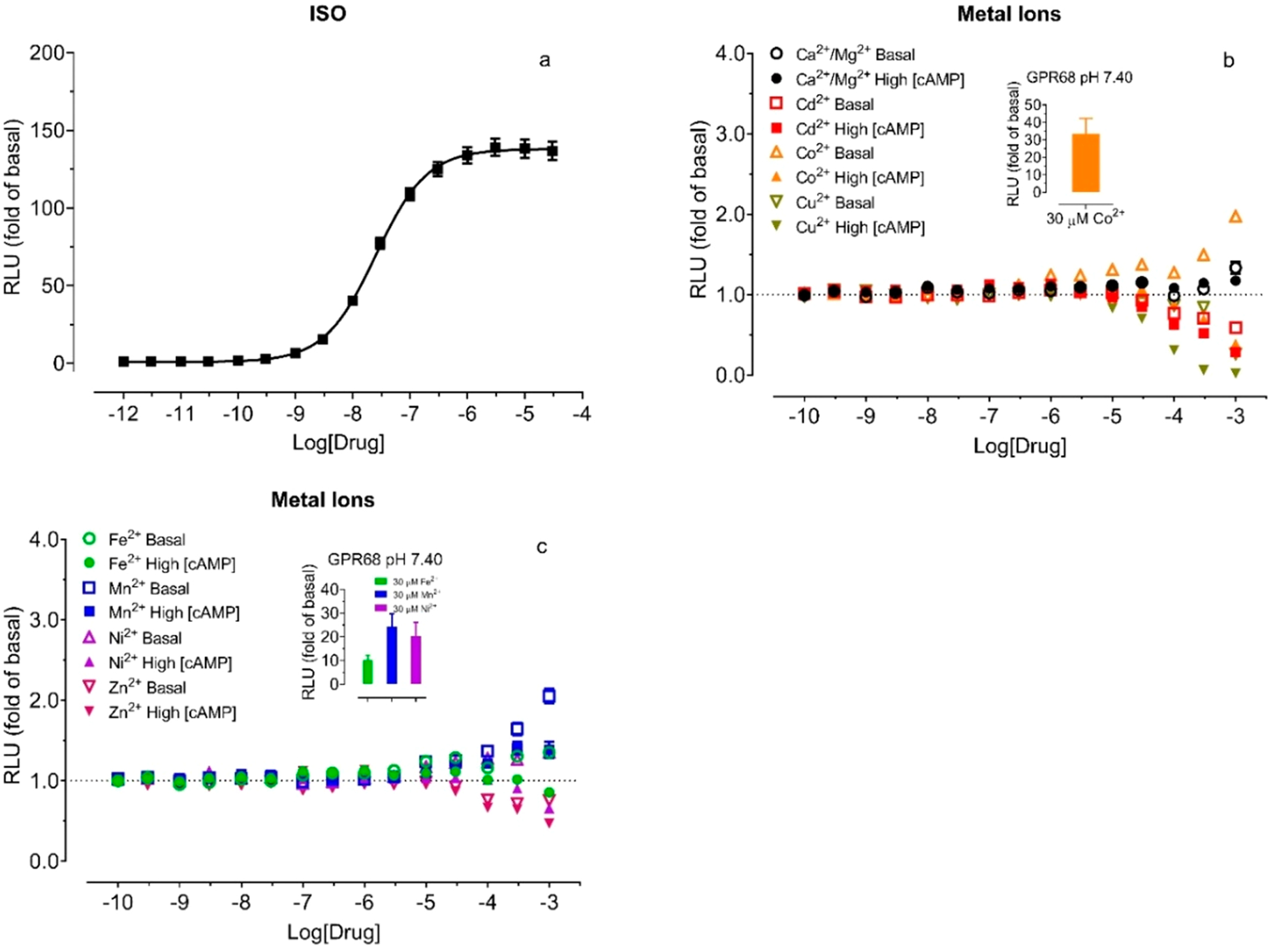
Effects of divalent metal ions on luciferase activity under basal and high concentrations of cAMP at control HEK293 T cells transiently transfected with the GloSensor cAMP reporter. The assays were conducted in the Ca2+/Mg2+-free HBSS-based buffer with 20 mM HEPES, 10 μM PDE inhibitor Ro 20–1724, pH 7.40, supplemented with indicated metal ions. (a) Isoproterenol (ISO) produced a concentration-dependent cAMP production through endogenous β2 adrenergic receptors, (b) Ca2+/Mg2+, Cd2+, Co2+, and Cu2+, (c) Fe2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+. Effects of metal ions were determined in the absence of ISO (basal) first and then in the presence of 0.3 μM ISO (high [cAMP]) in the same assay plate. Results were normalized to corresponding control (or basal) conditions in the form of the fold of basal and represented mean ± SEM from a minimum of 3 independent assays, each in a quadruplicate set. The curve was analyzed in Prism 8.4. For comparison, inserted bar graphs in panels b and c represented the activity of corresponding metal ions (fold of basal) at GPR68 at pH 7.40, with values from Table 2.
