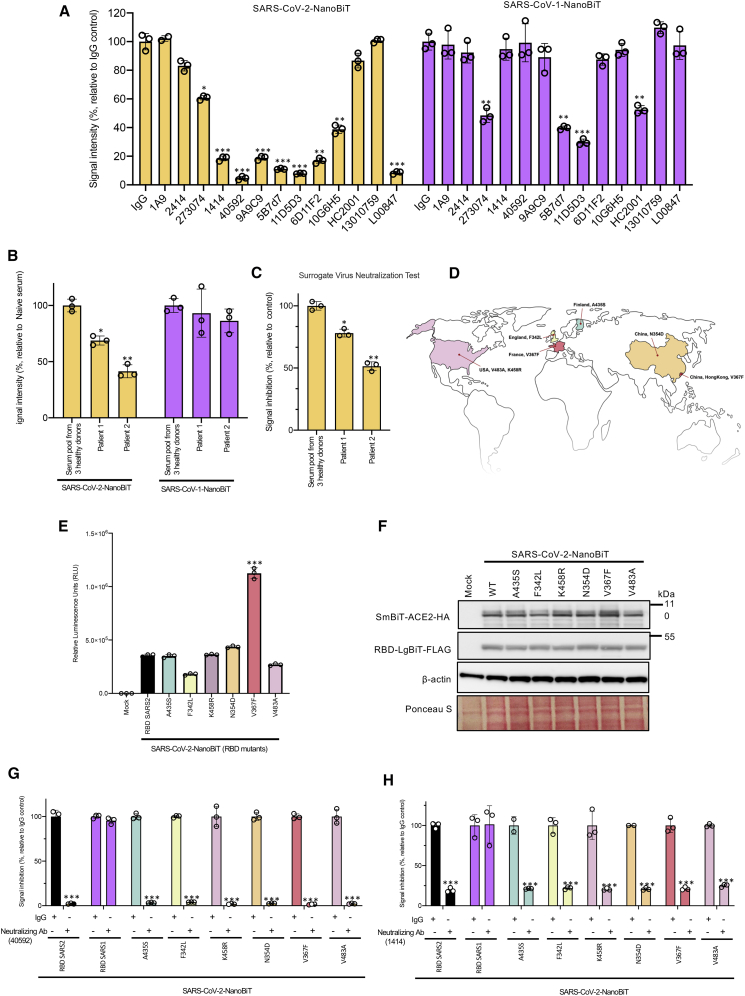
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2-NanoBiT enables facile detection of SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion
(A) SARS-CoV-2 (left) or SARS-CoV (right) bioreporter assays were performed with an array of anti-RBD monoclonal antibodies or control IgG. (B) SARS-CoV-2 BS (left) or SARS-CoV bioreporter (right) assays were performed with serum pooled from three healthy donors or two recovered SARS-CoV-2 patients for 25 min. A luciferase assay was performed 5 min after SmBiT-ACE2 addition. (C) SARS-CoV-2 RBD-HRP was incubated for 15 min with the serum pool from three healthy donors or recovered patients from SARS-CoV2 for 25 min. Then, samples were added to a plate coated with ACE2 for 15 min. After washing, tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) solution was added and the amount of RBD-HRP binding was evaluated by measuring the optical density (OD) at 450 nm. (D) Geographic distribution of the SARS-CoV-2 strains with the indicated RBD mutations. (E) BS assays were performed on cells co-transfected with the indicated RBD mutant-LgBiT constructs and SmBiT-ACE2 constructs. (F) Immunoblot analyses were performed to confirm the proper expression of the constructs. (G and H) Cell lysates transfected with different RBD-LgBiT mutants were incubated for 25 min with anti-RBD monoclonal antibodies 40592 in (G) and 1414 in (H). Luciferase assays were performed 5 min after SmBiT-ACE2 addition.