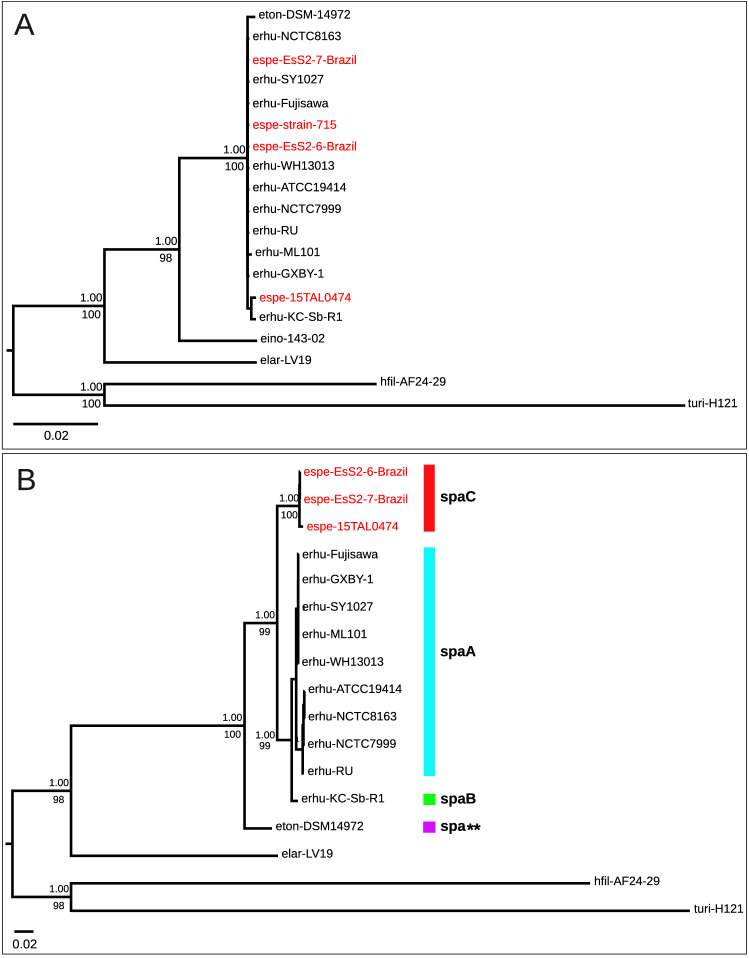
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of Erysipelothrix genus using single-genes. Legend: (A) Bayesian phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene under the model GTR+I+G. (B) Bayesian phylogenetic tree based on rpoB nucleotide sequence under the model GTR+I+G. Posterior probability values of support obtained in Bayesian Analysis (BA) are shown above nodes. Rapid bootstrap values obtained in Maximum Likelihood (ML) analysis are shown below nodes. Species were indicated as follows: E. sp. Strain 2 isolates (espe-EsS2-6-Brazil, espe-EsS2-7-Brazil, espe-15TAL0474, espe-strain-715); Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolates (erhu-ATCC19414, erhu-KC-Sb-R1, erhu-NCTC8163, erhu-NCTC7999, erhu-SY1027, erhu-GXBY-1, erhu-WH13013, erhu-Fujisawa, erhu-ML101, erhu-RU); Erysipelothrix inopinata strain 143-02 (eino-143-02); E. tonsillarum DSM 14972 (eton-DSM14972); E. larvae LV19 (elar-LV19); Holdemania filiformis AF24-29 (hfil-AF24-29); Turicibacter sp. H121 (turi-H121). Species hfil-AF24-29 and turi-H121 were used as outgroups. E. sp. Strain 2 isolates are shown in red.