Fig. 3.
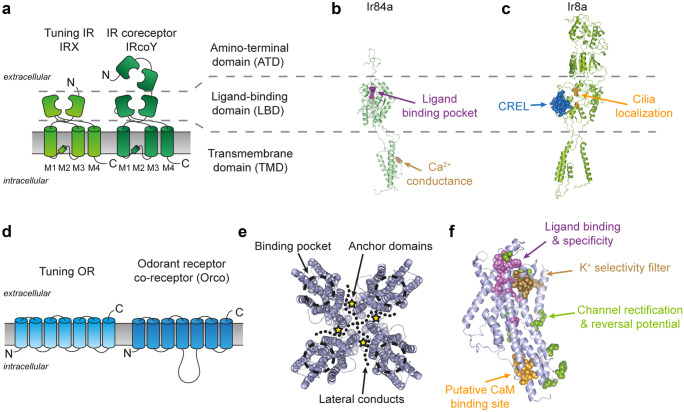
Structure-function of insect IRs and ORs. a Schematic representation of insect IRs. The functional unit of IRs is considered to be a heterotetramer made of two tuning receptor (IRX) and two coreceptor subunits (IRcoY) (Abuin et al. 2011; Abuin et al. 2019). The transmembrane domain (TMD) of both tuning receptor and coreceptor consists of four helices (M1-4). In the closely related AMPA ionotropic glutamate receptor (Croset et al. 2010), the re-entrant portion of the M2 loops forms the ion selectivity filter (Twomey et al. 2017). Both the tuning and coreceptor subunits possess the extracellular ligand-binding domain (LBD), but only the two coreceptors (i.e., Ir25a and Ir8a) possess an amino-terminal domain (ATD) (Croset et al. 2010). b–c Ribbon representation of a tuning (Ir84a) and a coreceptor (Ir8a) IR and characterized function of selected amino acid residues. b A glutamine in position 401 (in brown) in the M2 region of Ir84a is responsible for the Ca2+-dependent conductance of the Ir84a/Ir8a channels (Abuin et al. 2011). The LBD of tuning subunits houses the amino acid residues that form the ligand binding pocket and define the response specificity (Prieto-Godino et al. 2016; Prieto-Godino et al. 2017). In particular, for Ir84a see (Abuin et al. 2011; Cicconardi et al. 2017). c The LBD of the Ir8a coreceptor instead houses residues involved in the trafficking and correct cellular localization of the IR heteromers such as the coreceptor extracellular loop (CREL, in blue) (Abuin et al. 2019) and residues affecting IR localization to the sensory cilia (in orange) (Abuin et al. 2011). The coreceptor ATD also plays a major role in protein folding, heteromeric protein assembly, and/or cilia targeting (Abuin et al. 2011). Ir8a and Ir84a homology models were created in SWISS-MODEL (Waterhouse et al. 2018) with the R. norvegicus GluA2 structure (PDB: 6DLZ) (Twomey et al. 2018) as template following (Abuin et al. 2019). d Schematic representation of the 7 transmembrane-domain insect ORs. The functional unit of ORs is formed by heteromers made of a tuning OR and a coreceptor named Orco. e Top view ribbon representation of the tetrameric cryo-EM structure of Orco from the parasitic wasp Apocrypta bakeri (Butterwick et al. 2018). Highlighted are the binding pocket (dashed cicles), the anchor domain regions (star symbols), and the lateral conducts stemming from of the channel pore (dotted lines). f Functionally relevant residues of insect ORs, identified through mutagenesis studies, mapped on a Drosophila melanogaster Orco monomer. Critical residues are involved in the ligand binding and selectivity of ORs (in violet) (Corcoran et al. 2018; Hopf et al. 2015), a putative calmodulin binding site with modulatory function (Mukunda et al. 2014), K+ selectivity filter (in brown) (Wicher et al. 2008), and ion channel function (in green) (Hopf et al. 2015). The ribbon representation of D. melanogaster Orco was modeled on the A. bakeri cryo-EM structure using the I-TASSER server (Yang and Zhang 2015) and optimized using FoldX (Schymkowitz et al. 2005)