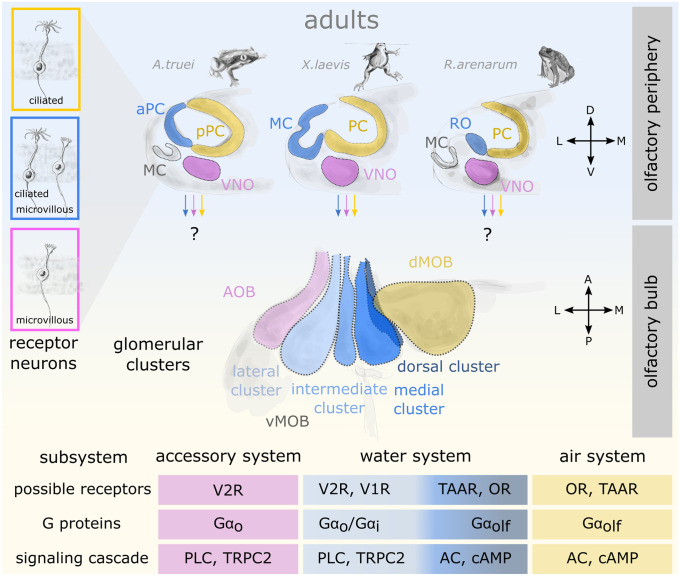
Fig. 4.
Anatomical, cellular, and molecular characteristics of the olfactory system in adult anurans. Above: Schematic coronal section of the left olfactory organs in the nasal cavities are shown for an archaeobatrachian (Ascaphus truei), a mesobatrachian (Xenopus laevis), and a neobatrachian frog (Rhinella arenarum). The main olfactory epithelium in adult anurans is segregated into a water- (blue) and an air-portion (yellow). While a major part of the principal cavity (PC) is lined with an air-type epithelium, the water-type epithelium is situated in different anatomical structures in the depicted species: anterior portion of the PC (aPC), middle cavity (MC), and recessus olfactorius (RO). The MC is non-sensory in most anurans. All species possess a vomeronasal epithelium in the VNO (purple). The boxes on the left show the types of receptor neurons present in each of the three epithelia. Middle: The respective axonal projections of the receptor neurons and their glomerular targets in the olfactory bulb show an anatomical segregation. Only the left hemisphere is shown. Due to incomplete comparative data, the scheme depicts the connectivity only for the genus Xenopus. While the VNO projects to the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB), the water-portion of the main olfactory epithelium (MC) projects to at least four clusters on the ventral surface of the main olfactory bulb (vMOB; shades of blue). The air-portion connects to the dorsal MOB (dMOB). Below: The putative molecular components linked to the above described olfactory subsystems are summarized based on data from the genus Xenopus and might show some inter-species variation that still needs to be uncovered. A anterior, AC adenylate cyclase, AOB accessory olfactory bulb, aPC anterior principal cavity, cAMP 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate, D dorsal, dMOB dorsal main olfactory bulb, L lateral, la lateral appendix, M medial, MC middle cavity, MOB main olfactory bulb, OR OR type olfactory receptor, P posterior, PC principal cavity, PLC phospholipase C, pPC posterior principal cavity, RO recessus olfactorius, TAAR trace amine-associated receptor, TRPC2 transient receptor potential channel 2, V ventral, V1R type 1 vomeronasal receptor, V2R type 2 vomeronasal receptor, vMOB ventral main olfactory bulb, VNO vomeronasal organ