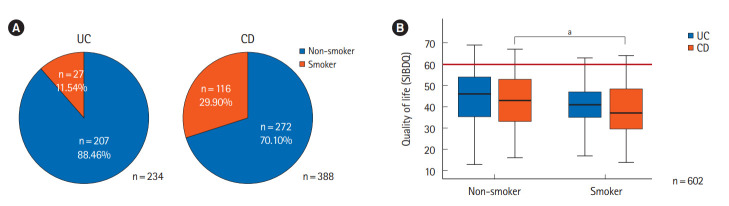
Fig. 4.
Smoking behavior and its influence on quality of life (QUOL) in IBD patients. (A) 11.54% (UC) to 29.90% (CD) of IBD patients currently smoke in our patient cohort. (B) Smoking reduces QUOL significantly in CD and by trend in UC. The boxplot’s median is depicted using a horizontal black line. Cutoff of the score for the QUOL was 60 points in the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (SIBDQ) and is depicted using a red line (≥60 normal QUOL, <60 moderately to severely reduced QUOL). A t-test was used for statistical analysis.aP<0.01. IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn’s disease.