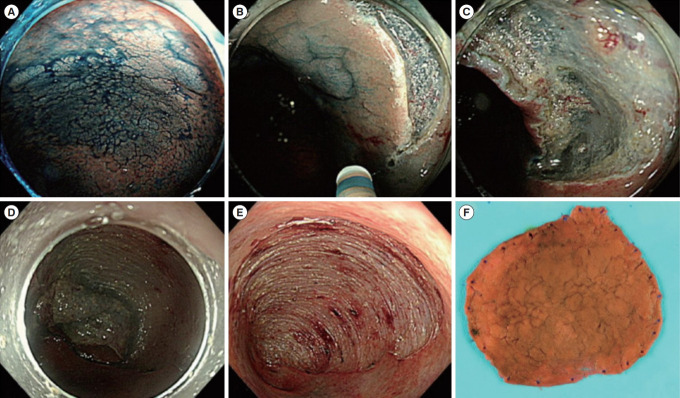
Fig. 3.
Representative example of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colitis-associated dysplasia. (A) Large, non-ulcerated Paris type O-IIa dysplasia with a distinct border in the rectum. (B) Mucosal incision was performed after submucosal injection. (C) Mild but diffuse submucosal fibrosis and submucosal fat deposition. (D-F) The colonoscope was changed into a gastroscope to expose the submucosal layer more effectively, and en bloc resection was achieved. The final histology revealed low-grade dysplasia (42×40 mm in size, with clear lateral and vertical margins). Adapted from Yang DH, et al. Clin Endosc 2019;52:120-128 [29].