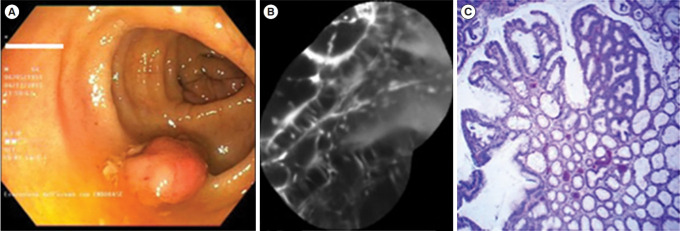
Fig. 4.
Dysplastic lesion. (A) White light endoscopic view showing a polypoid lesion (Paris 0-Is) of the transverse colon. (B) After resection and coloration with the 100 μM VRPMPLQ peptide solution, confocal laser endomicroscopy shows active binding of the peptide to dysplastic colonocytes is observed. This along with passive accumulation of the peptide determines an increase in fluorescence. (C) Conventional histology (H&E, ×106) showing low-grade dysplasia. VRPMPLQ is a synthetic peptide conjugated with fluorescein, which shows more selective binding to dysplastic tissue than to normal mucosa. Adapted from De Palma GD, et al. PLoS One 2017;12:e0180509 [67].