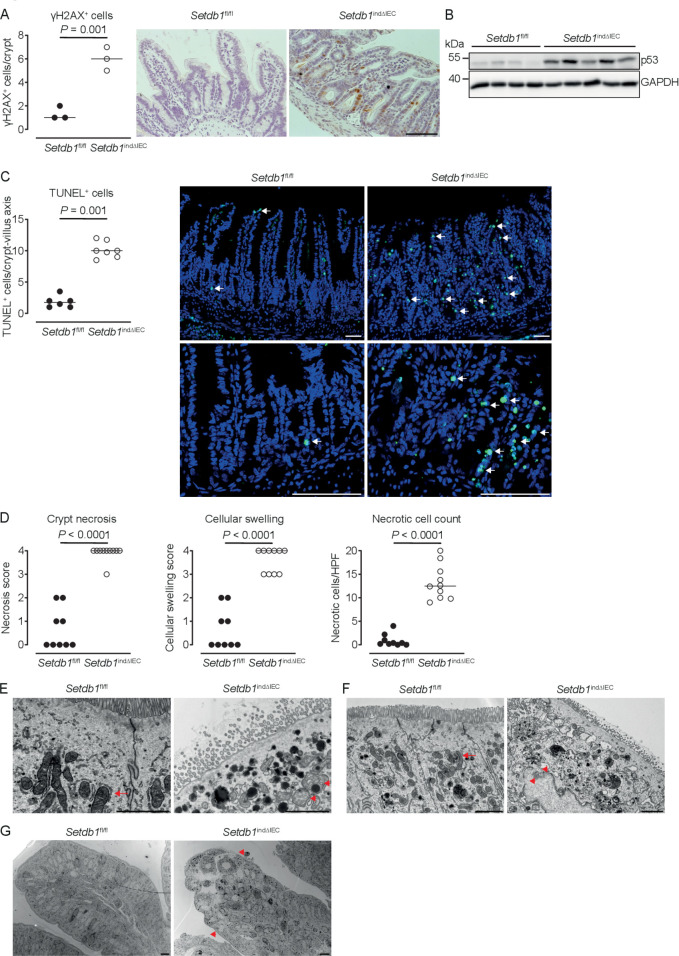
Figure 5.
Loss of epithelial SETDB1 is associated with DNA damage and cell death. (A) Percentage of histone H2AX phosphorylation (γH2AX)-positive cells per crypt as determined by immunohistochemical staining (left) and representative stainings (right) in the ileum of the indicated mouse strains. (B) Western blot analysis for p53 and GAPDH in small intestinal intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) of the indicated mouse strains. (C) Percentage of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells per crypt (left) and representative immunofluorescence stainings (right, TUNEL in green) in the ileum of the indicated mouse strains. Arrows show TUNEL-positive IECs. (D) Quantification of crypt necrosis and cellular swelling as well as of the number of necrotic cells per high power field in the ileum of the indicated mouse strains. (E–G) Representative electron microscopy images in the ileum of the indicated mouse strains. Arrows indicate normal mitochondria (E–F). Arrowheads indicated swelling and loss of the structural integrity of mitochondria (E) and loss of integrity of the nuclear membrane (F) as well as swelling of the cytoplasm and rupture of the plasma membrane (G). All data were obtained at day 10 after the first tamoxifen injection. Representative results of two independent experiments are shown (A–G). In (A, C–D), dots represent individual mice and the bar indicates the median. Size bars indicate 100 µm in (A, C), 2 µm (E, F), 10 µm (G). The Student’s t-test (A) or the Mann-Whitney U test (C–D) were applied. SETDB1, SET Domain Bifurcated Histone Lysine Methyltransferase 1, also known as ESET.