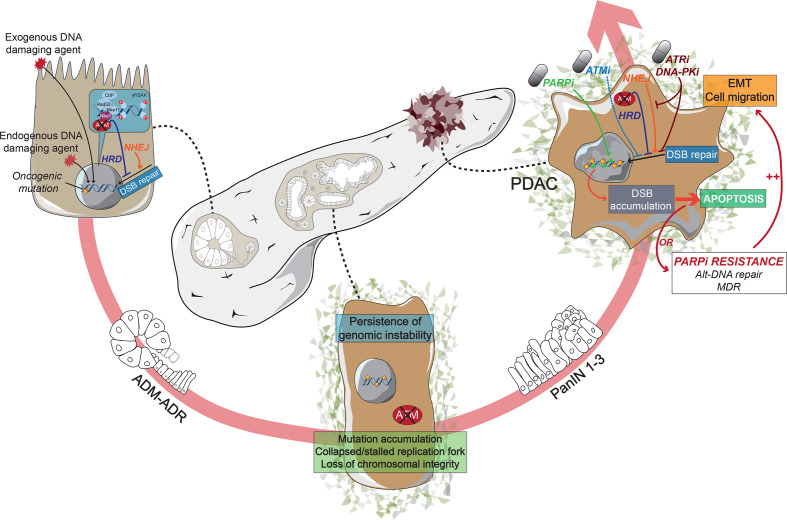
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of pancreatic cancer progression in a homologous recombination-deficient context. HRDness resulting from ATM deficiency sensitises pancreatic cells to exogenous and endogenous DNA damaging factors enabling an oncogenic cascade through acinar-to-ductal metaplasia. Sustained impaired double-strand break repair results in accelerated genomic instability driving the progression of preneoplastic PanIN stages to HRD pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Persistent HRD or therapeutically induced HRD by eg, ATMi renders cancer cells vulnerable to therapeutic interventions promoting DNA damage. Monotherapeutic approaches as PARPi subsequently tend to complex multidrug resistance (MDR) involving epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) and alternative DNA repair. Smart tailored use of synergistically druggable vulnerabilities within the DNA damage repair machinery could be exploited to hit HRD tumors “hard and early” and prevent further MDR acquisition, as eg, recently shown upon inhibition of PARP, ATR and DNA-PKcs.71 ADM, acinar-to-ductal metaplasia; ADR, acinar-to-ductal reprogramming; DSB, double-strand break; HRD, homologous recombination-deficient; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; PanIN, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia.