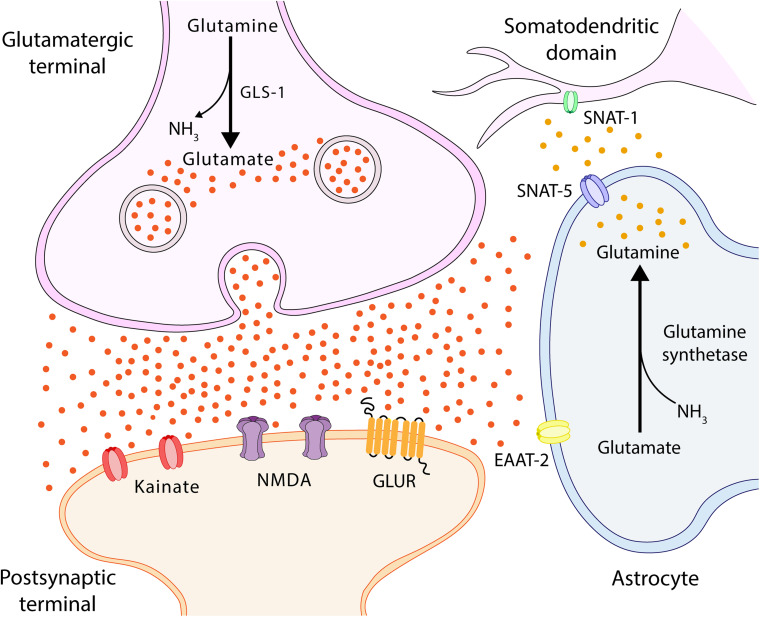
FIGURE 4.
Glutamate-glutamine cycle. Ammonia from the blood is neutralized in the astrocyte via a reaction with glutamate (Glu), which uses glutamine synthetase to form glutamine (Gln). Gln is transported by SNAT-5 to the extracellular environment, where it can then be transported to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or transferred to neurons by SNAT-1, located in the somatodendritic domain (Melone, 2004; Conti and Melone, 2006). In the neuron, Gln is degraded by phosphate-activated glutaminase (GLS-1) into Glu and ammonia. Glu feeds the neurotransmitter pool and is released into the synaptic cleft, interacting with Glu receptors located in both synapses and astrocytes. SNAT-1, neuronal glutamine transporter; SNAT-5, astrocytic glutamine transporter-5; and EAAT, excitatory amino acid transporter.