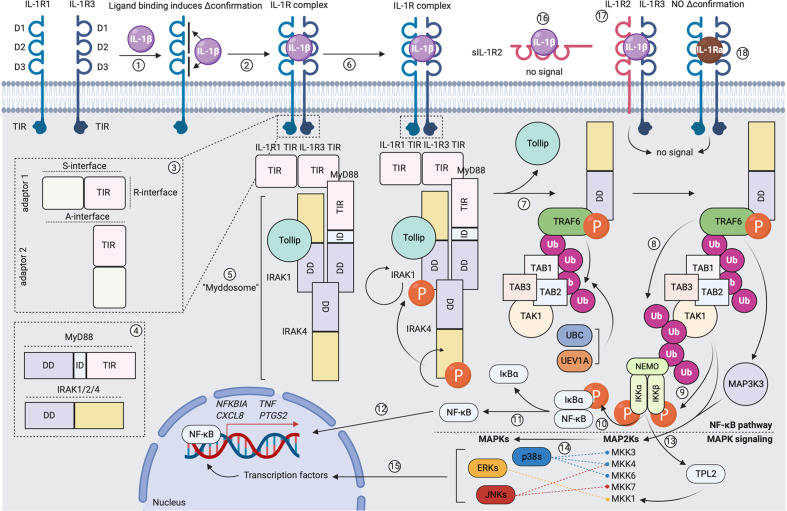
Figure 3.
Formation of the signaling-competent IL-1R complex and downstream IL-1 signaling. (1) Extracellular IL-1β makes two contacts with IL-1R1 and induces a conformational change in the primary receptor. (2) This allows IL-1R1 to recruit and bind to co-receptor IL-1R3. (3) Receptor dimerization leads to scaffolding of intracellular receptor TIR domains via the R-interface. (4) and (5) Formation of an intracellular TIR scaffold allows for recruitment of the MyD88 adaptor molecule via S-interface interactions. MyD88 comprises an N-terminal death domain (DD), an intermediate domain (ID) and a C-terminal TIR domain. IRAK-1, IRAK-4 and/or IRAK-2 are recruited. These molecules comprise an N-terminal DD and a C-terminal catalytic domain. Under steady-state, IRAK-1 is bound to Tollip. As such, the Myddosome is formed. (6) IRAK-4 auto-phosphorylates and gains full activity, in turn activating IRAK-1 by phosphorylation. This induces rapid IRAK-1 auto-phosphorylation. (7) A conformational change in IRAK-1 allows its dissociation from Tollip. Different IRAK-1 oligomers form a scaffold for TRAF6, which becomes activated upon oligomerization. UBC13 and UEV1A facilitate TRAF6 self-poly-ubiquitination (K63-linked). TAB2 and TAB3 recruit TAB1 and the MAP3K TAK1 to the K63-linked poly-ubiquitin chain on TRAF6. (8) TRAF6 poly-ubiquitinates TAK1. (9) Initiation of the canonical NF-κB pathway: NEMO binds to the poly-ubiquitin chain on TAK1 and recruits IKKα and IKKβ. IKKα and IKKβ become activated following phosphorylation by TAK1. (10) and (11) IKKα and IKKβ phosphorylate IκBα, which allows for its dissociation from p50/p65 NF-κB. (12) Free p50/p65 NF-κB translocates to the nucleus and binds to specific κB sites on DNA, as such inducing gene expression. (13) Initiation of the MAPK pathway: the MAP3K MAP3K3 binds the poly-ubiquitin chain on TAK1. MAP3K3 becomes activated following phosphorylation by TRAF6. IKKα and IKKβ activate TPL2 by phosphorylation. MAP3K3, TAK1 and TPL2 activate different MAP2Ks by phosphorylation. (14) MAP2Ks activate the p38, JNK and ERK MAPKs by phosphorylation. (15) In turn, MAPKs activate different transcription factors by phosphorylation, as such inducing gene expression. (16) Binding of IL-1β to sIL-1R2 does not induce signal transduction. (17) Binding of IL-1β to the signaling-incompetent IL-1R complex does not induce signal transduction. (18) Binding of IL-1Ra to the signaling-competent IL-1R complex does not induce signal transduction. Created with BioRender.com.