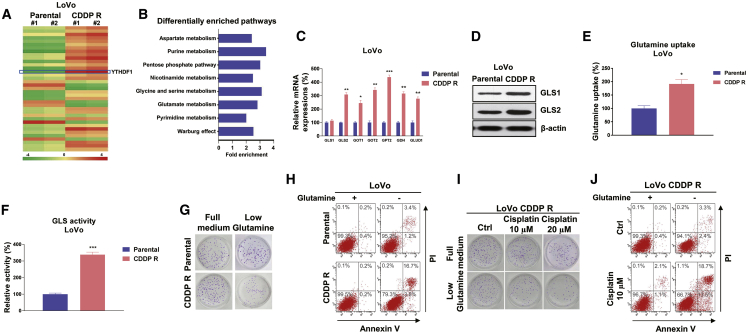
Figure 3.
Cisplatin-resistant CRC cells exhibit elevated glutamine metabolism
(A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes from LoVo parental and CDDP R cells identified by RNA-seq. (B) MetaboAnalyst pathway enrichment analysis of metabolites in LoVo parental and CDDP R cells. (C) mRNA expression levels of glutamine metabolism enzymes and regulators were detected by qRT-PCR in LoVo parental and CDDP R cells. (D) Western blot results show protein expression of GLS1 and GLS2 in LoVo parental and CDDP R cells. (E and F) Glutamine uptake (E) and GLS activity (F) assays were performed in LoVo parental and CDDP R cells. (G) LoVo parental and CDDP R cells were cultured with regular medium or glutamine depletion medium, a clonogenic assay and (H) annexin V assay were performed. (I) LoVo CDDP R cells cultured with regular medium or glutamine depletion medium were treated with cisplatin at 10 and 20 μM for 48 h. (J) Cell viability and cell death were examined by a clonogenic assay and (H) annexin V assay. Columns include mean of three independent experiments; data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.