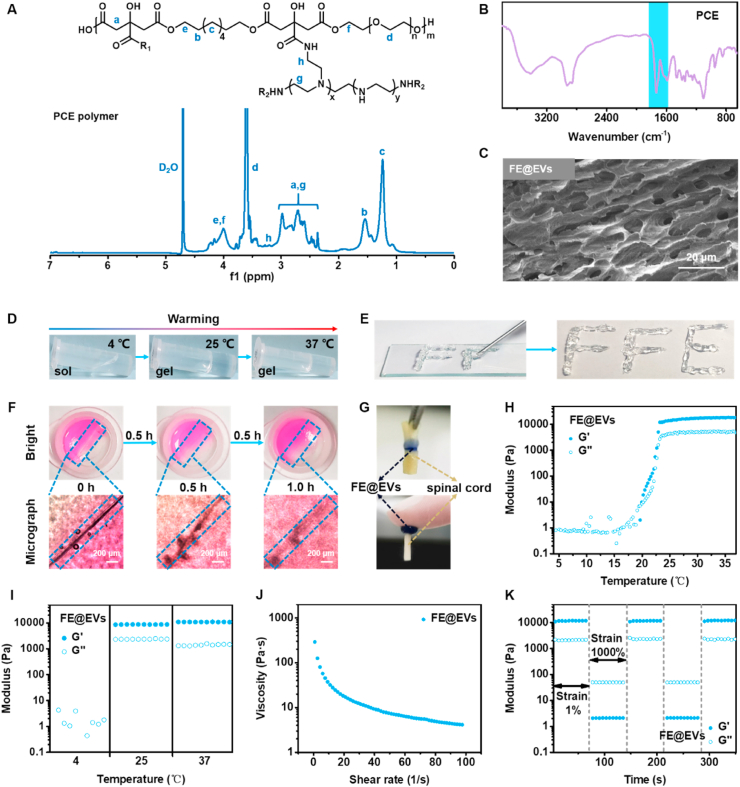
Fig. 1.
Physicochemical structure and multifunctional properties of FE@EVs hydrogel. (A) 1H NMR spectra of PCE polymer; (B) FTIR spectra of FE hydrogel. (C) SEM image of FE@EVs hydrogel. (D) The sol-gel transition of FE@EVs hydrogel with temperature changes. (E) The photographs of FE@EVs hydrogel through the needle. (F) The photographs of FE@EVs hydrogel placed for a while after being cut off. (G) The photographs of FE@EVs hydrogel adhering to spinal cord. (H) The G′ and G″ changes of FE@EVs hydrogel at 4 °C–38 °C; (I) The G′ and G″ of FE@EVs hydrogel at 4, 25 and 37 °C within 1 min; (J) The viscosity changes of FE@EVs hydrogel at 1 1/s to 100 1/s shear rate. (K) The G′ and G″ changes of FE@EVs hydrogel after two cycles of step strain.