Figure 4. Macrophage uptake reduces the hepatotoxicity of nanotherapeutics.
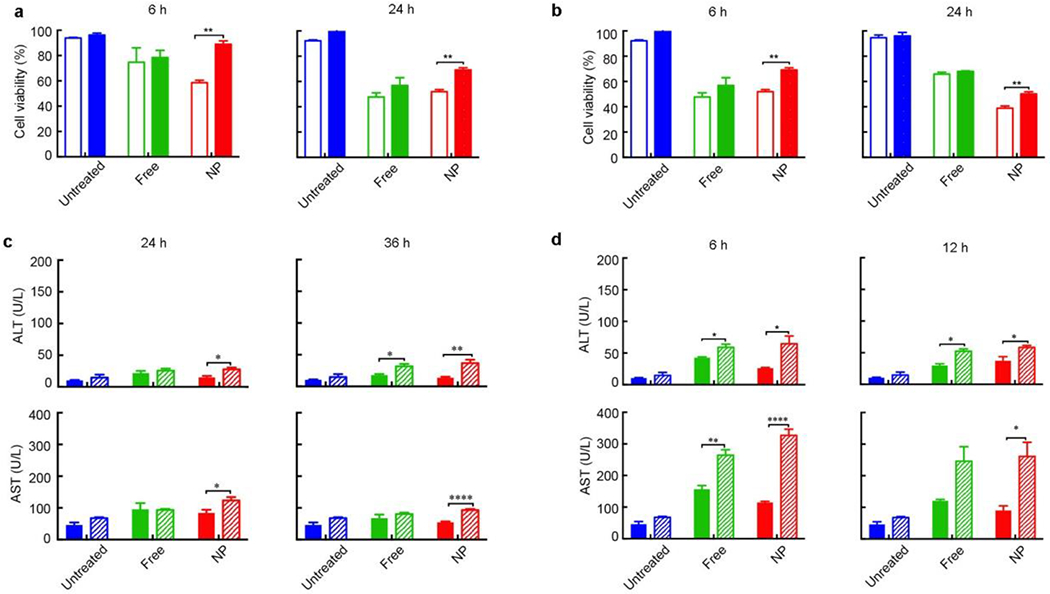
a, b, In vitro cytotoxicity of primary hepatocytes cultured in liver matrix coated plates. The hepatocytes were treated with free CPZ and CPZ-loaded NPs (NP) (a) or free Wtmn and Wtmn-loaded NPs (b) without (hollow columns) or with (solid columns) macrophage incubation. The cytotoxicity was analyzed by MTS assay 6 h and 24 h after treatments. Data represent mean ± SEM. (n = 6). Statistical significance was assessed using the Mann Whitney test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. c, d, In vivo hepatotoxicity in CD-1 mice treated with free CPZ and CPZ-loaded NPs (c) or free Wtmn and Wtmn-loaded NPs (d). The mice were either without (solid columns) or with (stripe columns) macrophage depletion. The hepatotoxicity was analyzed by ALT and AST 24 h and 36 h after treatment with free CPZ and CPZ-loaded NPs, or 6 h and 12 h after treatment with free Wtmn and Wtmn-loaded NPs. Data represent mean ± SEM. (n = 8-10). Statistical significance was assessed using the Mann Whitney test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
