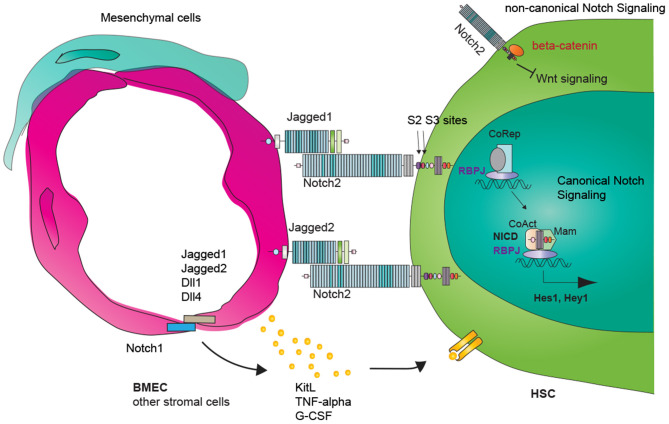
Figure 1.
Vascular Notch regulation of adult hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) maintenance and regeneration. Canonical Notch signaling involves ligand and receptor binding, Notch receptor subsequent cleavages and release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD). NICD translocates into the nucleus and turns on RBPJ/NICD-dependent transcription (canonical Notch signaling). RBPJ-independent NICD function is defined as non-canonical Notch signaling. Vascular endothelial cells express Notch ligands Jagged1, Jagged2, Dll1, Dll4, and Notch receptors. Vascular Notch ligand induces Notch downstream target expression within HSCs (cell-autonomous). Notch signaling within endothelial cells could lead to changes in inflammatory signaling and paracrine secretome, including TFN-alpha, GCSF, and KitL, which could then impact HSC behavior cell non-autonomous.