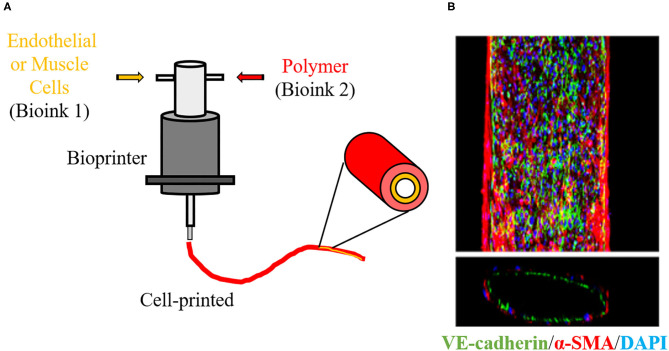
Figure 6.
3D Bioprinter. (A) Schematic overview of 3D cell printing technique to create a vascular graft using bioinks. 3D bioprinter deposit polymers with living cells layer-by-layer in a desired structure, allowing to create a vascular architecture with endothelial and smooth muscle layers. (B) Immunofluorescence staining image show that a 3D-bioprinted vascular graft is constructed of endothelial cells (green) and smooth muscle cells (red). Blue indicates nuclear. The image is adapted from a report by Gao (76).