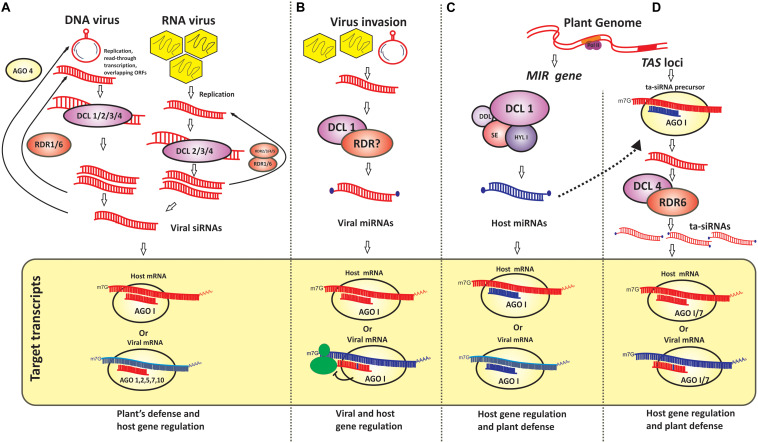
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of viral and host-derived small RNAs and their regulatory role (A) Viral genome-derived small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) from plant infecting DNA and RNA viruses and their role in regulation of plant gene expression and viral gene downregulation are presented. Host protein components such as dicer-like enzymes (DCL)1 through 4 and argonaute protein (AGO) 1, 2, 5, 7, and 10 participate in this process; (B) Viral genome-derived microRNAs (miRNAs) and their regulatory role in modulating the expression of virus genes as it may also function as miRNA mimic to downregulate host mRNA causing the host’s susceptibility. Although little is known about the role of plant proteins in the generation of viral-derived miRNAs this mode of pathogen’s virulence is well recognized in animal-virus interactions; (C,D) Host-derived microRNAs and trans-acting siRNAs (miRNAs and tasiRNAs) and their role in plant gene regulation and host defense are depicted. Host DCL1 and AGO1 are known in miRNA generation whereas the activities of DCL4, RDR 6, and AGO1, AGO7 are known in tasiRNA mediated gene regulation.