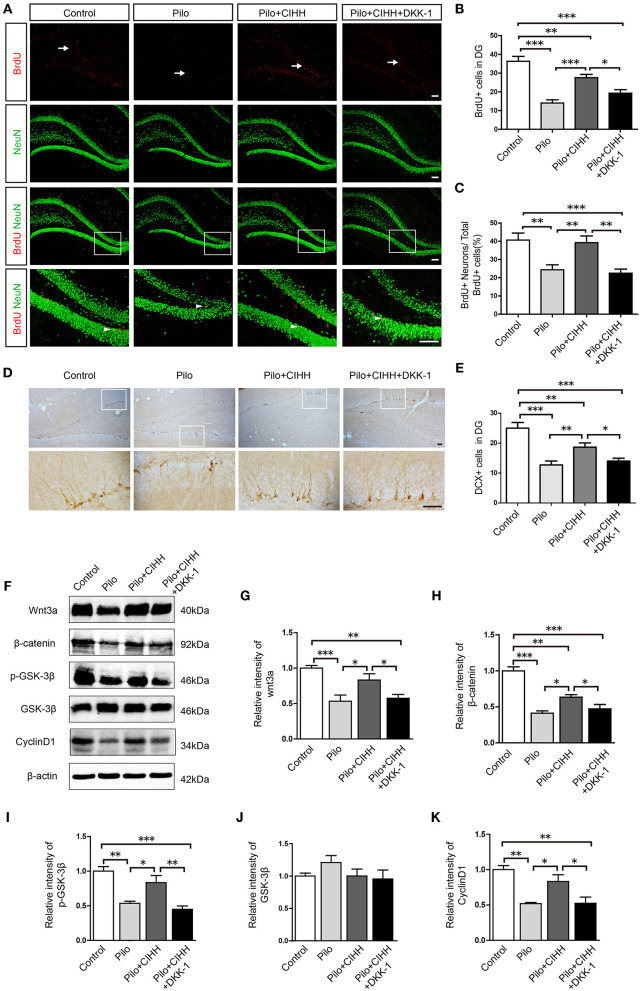
Figure 5.
The Wnt inhibitor DKK-1 reduces CIHH-induced hippocampal neurogenesis and downregulates Wnt/β-catenin pathway protein expression in epileptic hippocampi. (A) Representative images of BrdU (red)/NeuN (green) immunostained cells in the DG of each group. White arrows indicate BrdU+ cells and white arrowheads indicate BrdU+/NeuN+ cells. (B) The number of BrdU+ cells in the DG was reduced by epilepsy and rescued by CIHH but not by CIHH + DKK-1. (C) Proportion of BrdU+/NeuN+ cells to the total number of BrdU+ cells (%) showing a similar pattern. (D) Representative DG cells immunostained with the immature neuronal marker DCX from each group. (E) The number of DCX+ cells in the DG region was reduced by epilepsy and rescued by CIHH but not by CIHH + DKK-1. (F) Representative images of western blots for Wnt/β-catenin pathway protein expression levels in the hippocampus. (G–K) Relative intensities of Wnt and β-catenin expression in the hippocampus. All values are normalized to the control samples and reveal suppression by epilepsy and rescue by CIHH but not by CIHH + DKK-1. All values are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. n = 3 rats per group. (A) Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Scale bar, 50 μm.