Figure 1.
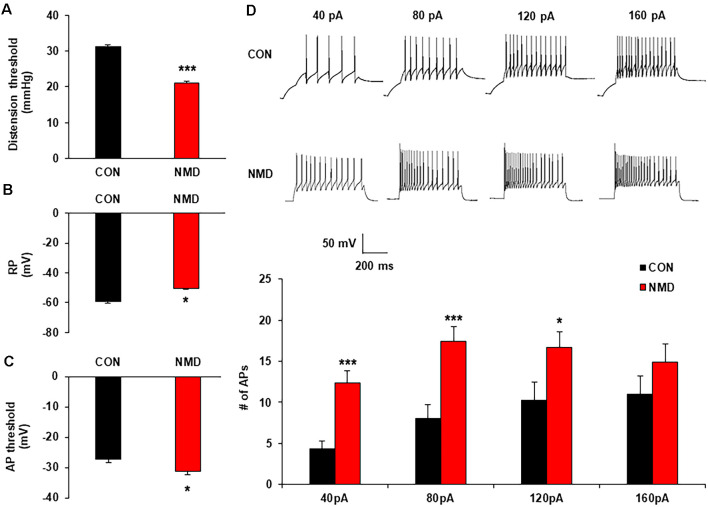
Neonatal maternal deprivation (NMD) reduced visceral pain threshold and enhanced the neuronal excitability. (A) NMD rats developed chronic visceral pain (***P < 0.001, n = 6 rats for each group, Tukey post hoc test following two-way repeated measures ANOVA). (B) NMD depolarized the resting membrane potential (RP; *P < 0.05, n = 17 cells for CON and n = 15 cells for NMD, two sample t-test). (C) NMD hyperpolarized the threshold of action potential (AP) in NMD rats when compared with CON (*P < 0.05, n = 10 cells for CON and n = 17 cells for NMD, two sample t-test). (D) NMD significantly enhanced the frequency of AP method under 40, 80, and 120 pA ramp current stimulation (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, n = 17 cells for CON and n = 15 cells for NMD, two sample t-test).