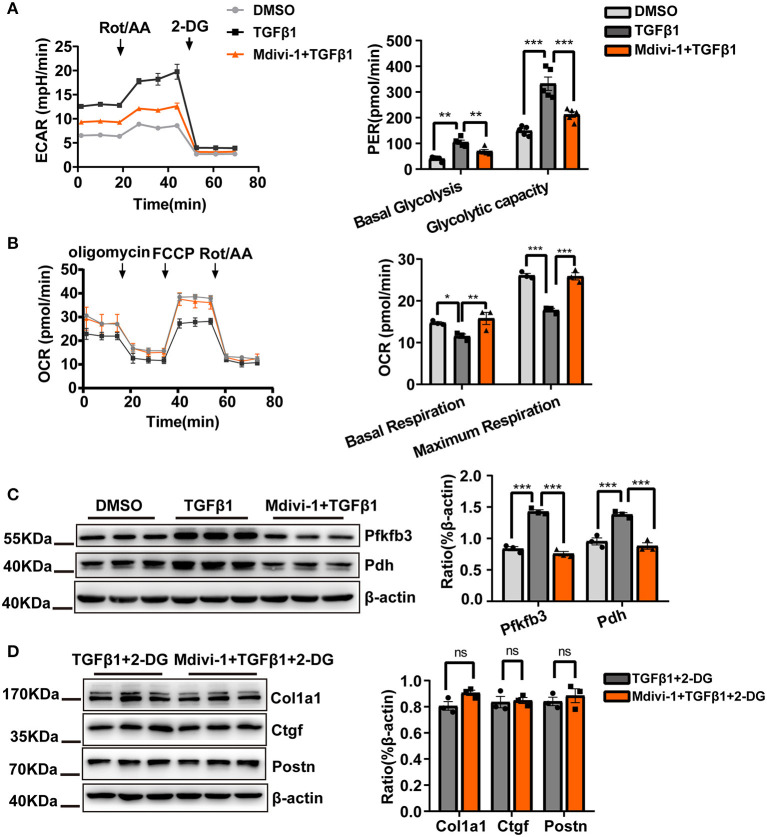
Figure 3.
Reducing the cardiac fibroblasts (CF) glycolytic flux may be important for mitochondrial fission inhibition-induced suppression of CF activation. (A) Measurements of the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) metabolic profile by Seahorse XF glycolytic rate assay kit and analyses of CF Proton Efflux Rate (PER) in basal glycolysis and glycolysis capacity. (B) The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) as measured using a Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit and analyses of the OCR under basal and maximum respiration. (C) Western blot analyses and quantification of key glycolytic enzymes under TGF-β1 plus mdivi-1 cotreatment. (D) The expression of CF activation-related markers was measured by immunoblotting following TGF-β1 plus mdivi-1 cotreatment and in the presence or absence of 2-DG. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 independent cell isolations per group). Means were compared by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) post hoc test. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.