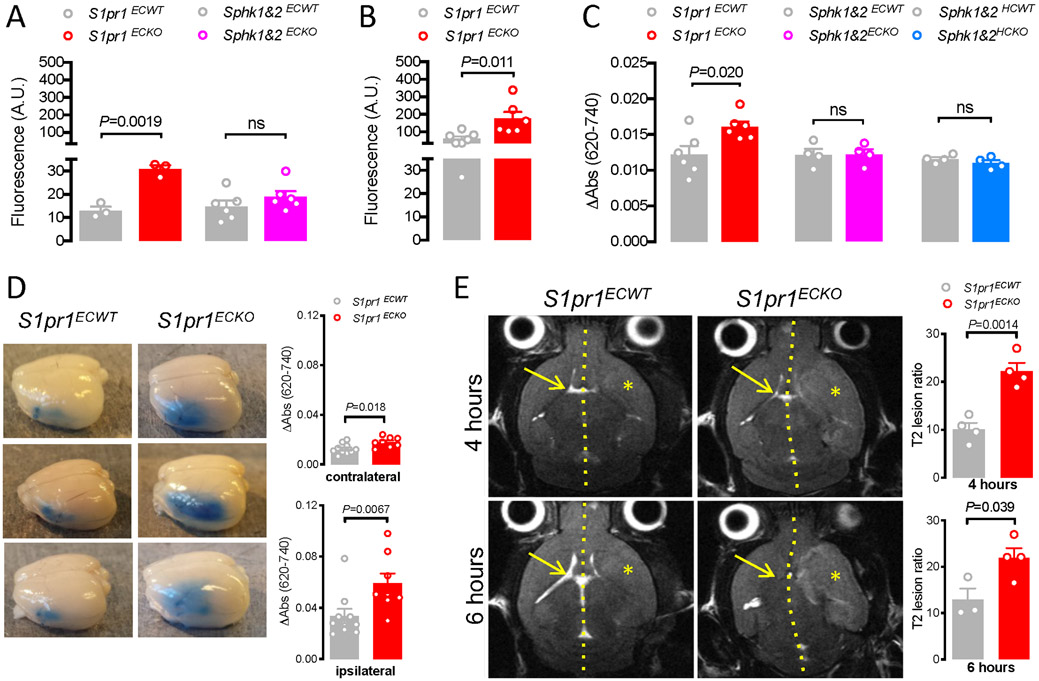
Figure 4. Endothelial S1P1 sustains BBB function.
A. Effect of Pdgfb-iCreERT2-mediated deletion of S1pr1 and Sphk1&2 on the accumulation of 4 kD TRITC-Dextran in the cerebral cortex of naïve mice. B. Effect of Pdgfb-iCreERT2-mediated deletion of S1pr1 on the accumulation of 4 kD TRITC-Dextran in the cerebral cortex 8 hours after challenge with 10 mg/kg LPS i.p. C. Effect of Pdgfb-iCreERT2-mediated deletion (ECKO) of S1pr1 and Sphk1&2 as well as Mx1-Cre-mediated deletion (HCKO) of Sphk1&2 on the accumulation of Evans Blue/albumin in the brain of naïve mice. D. Effect of Pdgfb-iCreERT2-mediated deletion of S1pr1 on Evans Blue/albumin leak 24 hours after pMCAO in ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. Left, representative brains. Right, corrected absorbance of full hemisphere extracts. E. Full T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 4 and 6 hours after 90 min tMCAO in S1pr1ECKO and littermate controls. Left: Representative axial sections from level of the mid-olfactory bulb from the same animal at the two time points. Hatched line indicates midline, asterisk affected MCA territory, and arrow contralateral ventricle. Right: T2 lesion ratios calculated from MRI images based on axial plane images at the mid-olfactory bulb. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM. Statistical significance assessed by Mann-Whitney test (D) and unpaired t-test (all other).