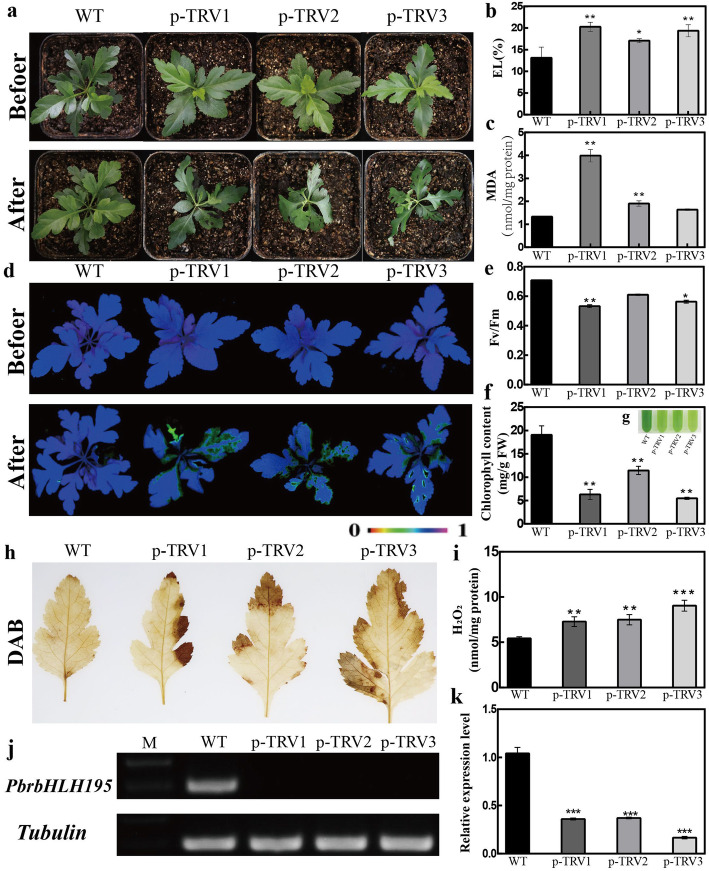
Fig. 6.
Cold tolerance assay of PbrbHLH195-silenced Pyrus betulaefolia plants. a-c Phenotype of 1-month-old PbrbHLH195-silenced plants before and after cold treatment for 8 days (a). Electrolyte leakage (EL) (b) and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations (c) after cold treatment. d-g Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging of silenced plants and WT plants(d), Fv/Fm ratios (e), Chl content (f) and phenotype (g) of WT and pTRV-PbrbHLH195 silencing plants (pTRV-1, pTRV-2 and pTRV-3) at the end of the chilling stress. h-i In situ accumulation of H2O2 of WT and silencing plants, as revealed by histochemical staining with 3, 3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) (h) after cold treatment. Quantitative measurement of H2O2 (i) levels after cold treatment. The expression of PbrbHLH195 was detected by RT-PCR (j) and qRT-PCR (k) at 8d after cold treatment