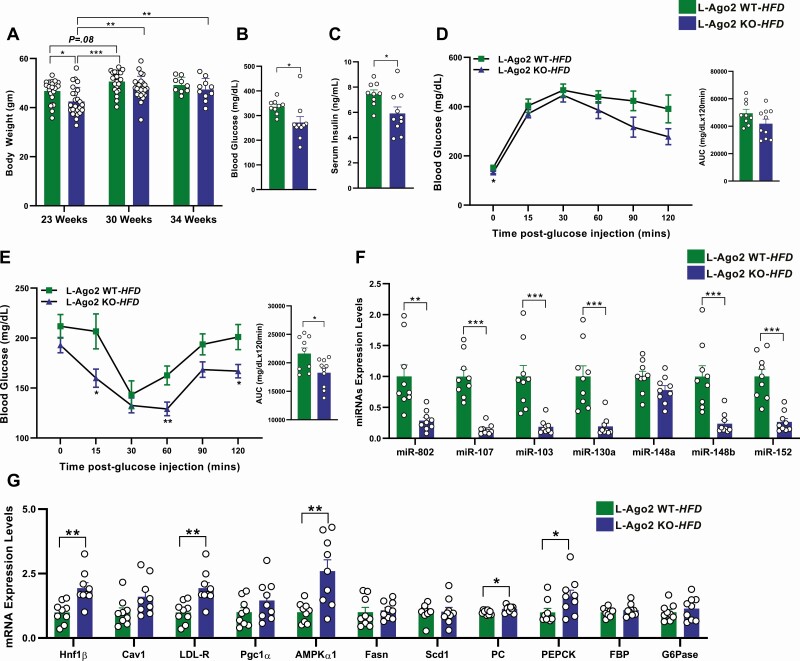
Figure 2.
Effect of hepatic Argonaute 2 (Ago2) deficiency on glucose metabolism in a long-term high-fat diet (HFD) condition. A, Body weight of liver-specific Ago2-deficiency (L-Ago2) wild-type (WT) and L-Ago2 knockout (KO) mice on an HFD at age 23 (n = 22 and 25, respectively), 30 (n = 22 and 25, respectively), and 34 (n = 9 and 10, respectively) weeks. B, Blood glucose levels after 6 hours of fasting of L-Ago2 WT (n = 9) and L-Ago2 KO (n = 10) mice at age 34 weeks. C, Serum insulin levels of L-Ago2 WT (n = 9) and L-Ago2 KO (n = 10) mice at age 34 weeks. D, Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and its area under the curve (AUC) analysis in L-Ago2 WT (n = 9) and L-Ago2 KO (n = 10) mice at age 30 weeks. E, Insulin tolerance test (ITT) and its AUC analysis in L-Ago2 WT (n = 9), and L-Ago2 KO (n = 10) mice at age 31 weeks. F, Metabolic disease–associated microRNAs (MD-miRNAs) and their G, target messenger RNA (mRNA) expression levels in livers of L-Ago2 WT (n = 9) and L-Ago2 KO (n = 9) mice at age 34 weeks. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of group size (n). Statistical analyses were performed by ordinary one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey post hoc test for A or unpaired 2-tailed test for B to G. *P less than or equal to .05, **P less than or equal to .01, ***P less than or equal to .001.