Figure 7: Proposed structure of Mabs LAM, consistent with available data.
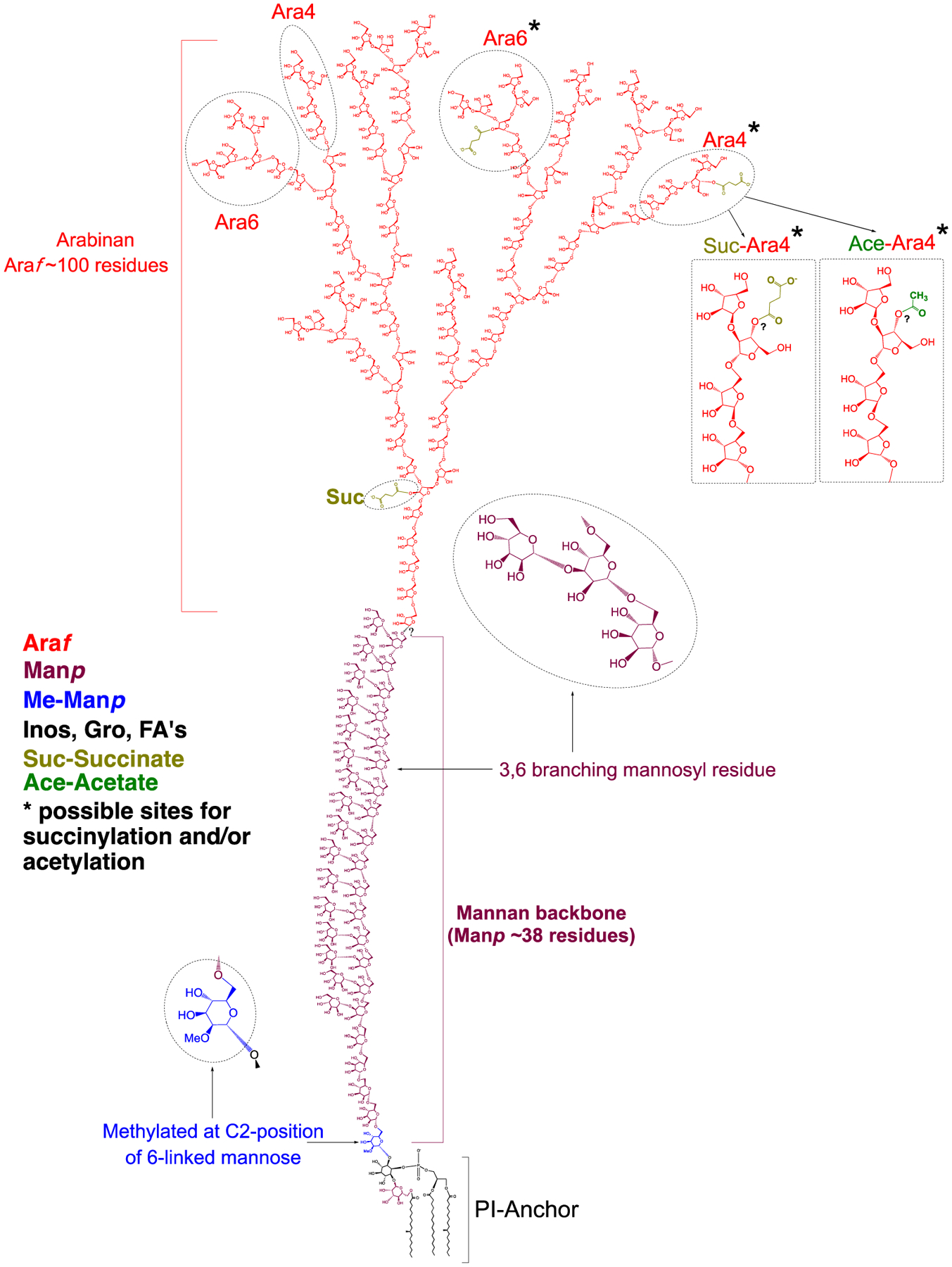
The non-reducing arabinan termini of Mabs LAM are devoid of capping residues. The core structure of the arabinan domain consists of ~ 100 D-Araf residues including linear α−1,5-linked residues and α−1,3 branch points. The arabinan domain is terminated with β-D-Araf-1,2-α-D-Araf at the non-reducing end and there is an equal proportion of linear Ara4 and branched Ara6 arabinan termini. Succinyl residues substitute both internal and terminal arabinosyl residues whereas acetyl residues substitute terminal arabinosyl residues. The precise positions of the succinyl and acetyl residues substituting the terminal arabinosyl residues are currently not known. The mannan backbone with 38 α-D-Manp residues (dominant species per Figure 3A) is composed of linear α−1,6-linked residues and α−3,6 branch points. A single α−1,6-linked Manp residue located at the reducing end of the mannan backbone is methylated at the C-2 position. Further analyses are required to determine the covalent linkage of the arabinan domain to the mannan backbone and the precise structural organization of these two domains. Inos, Inositol; Gro, glycerol; FA, fatty acyl chains.
