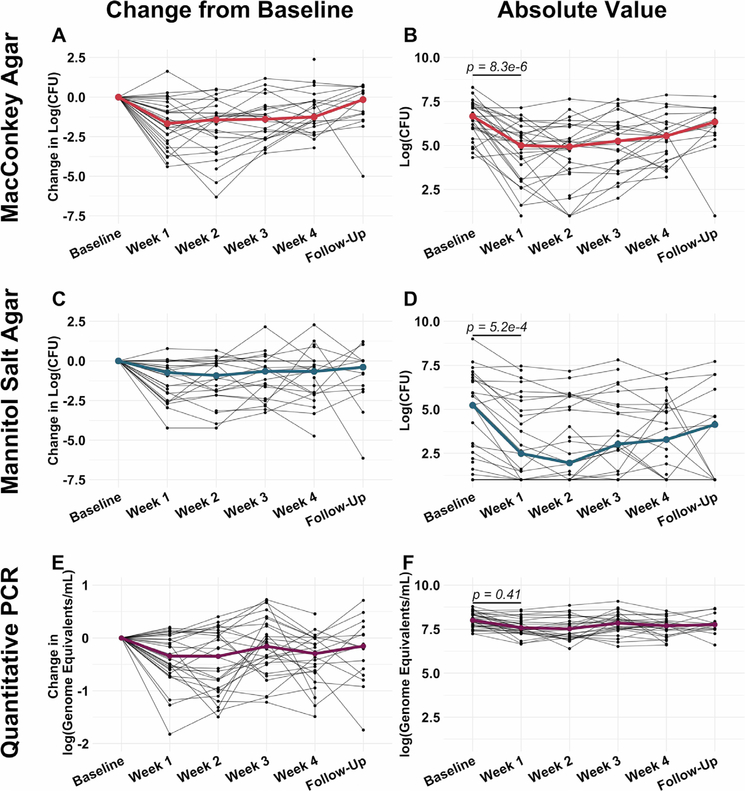
Figure 1.
Intersubject variability of sputum microbiological responses to a cycle of maintenance inhaled tobramycin was greater than intrasubject variability. (A and B) Change in culturable colony counts on MacConkey agar (sequencing-based analyses demonstrated these to be predominantly Pseudomonas aeruginosa with minor contributions of Serratia marcescens, Stenotrophomonas maltophila, Achromobacter xylosoxidans and an unidentified yeast taxon) from baseline (A) and absolute viable counts (B) by week on therapy. (C and D) Similarly show change in viable counts on mannitol salt agar (Staphylococcus aureus) from baseline (C) and absolute viable counts by week on therapy (D). (E and F) Change in TBL from baseline (E) and absolute TBL, (F) by week on therapy. Black lines represent individual subjects and coloured lines indicate medians. Baseline samples were collected prior to starting therapy, weeks 1–4 represent weekly samples collected during therapy and follow-up samples were collected 1 month after cessation of therapy. P values were determined using a Wilcoxon signed rank sum test comparing baseline and week 1 values. All values are presented after log transformation. TBL, total bacterial load.