Figure 5.
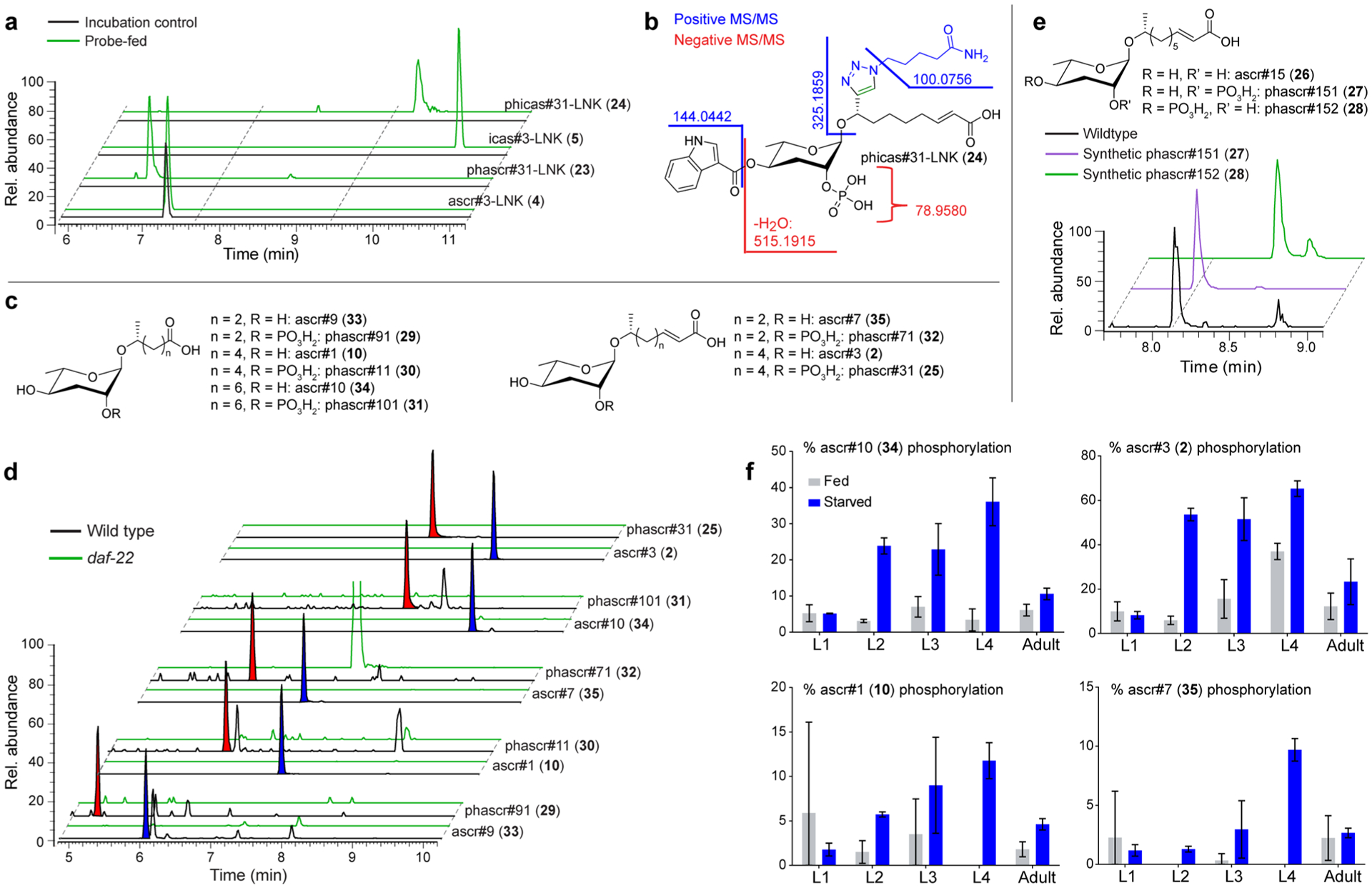
Identification of phosphorylated PDMs. (a) EICs for features representing phosphorylated PDMs in probe-fed and incubation control data sets. (b) MS/MS analysis of phicas#31-LNK (24). (c) Structures of simple ascarosides and their phosphorylated derivatives. (d) EICs for compounds in panel (c) in wildtype and daf-22 exo-metabolomes reveal extensive phosphorylation of ascarosides. Phosphorylated and corresponding nonphosphorylated ascaroside species are highlighted with red and blue shading, respectively. (e) EICs for synthetic phascr#151 (27), synthetic phascr#152) (28), and the phosphorylated ascr#15 in wild-type exo-metabolome indicates phosphorylation at the 2′-position. (f) Abundances of phosphorylated ascarosides relative to corresponding nonphosphorylated ascarosides in different life stages.
