Figure 6.
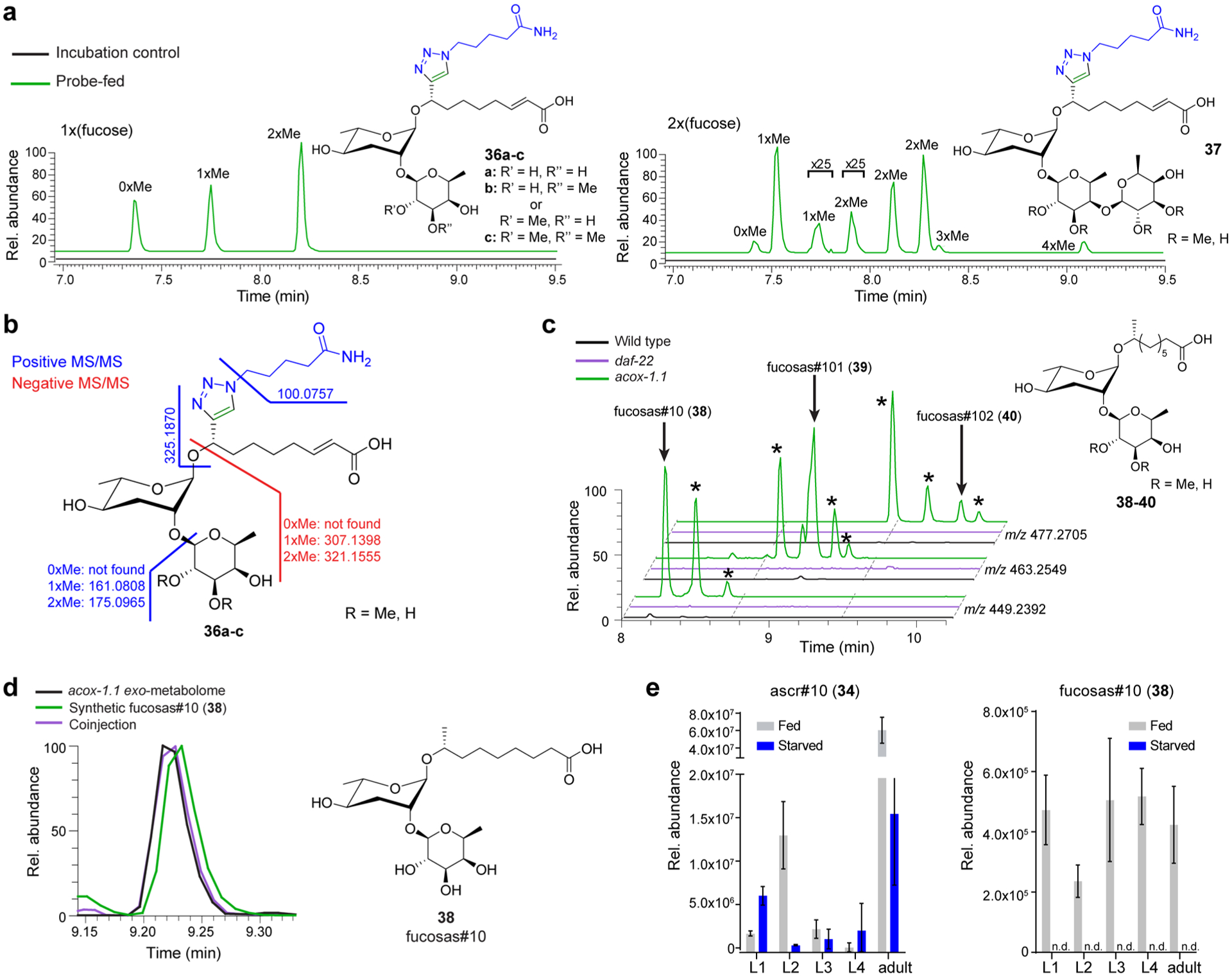
Identification of PDMs representing fucosylated ascarosides. (a) EICs for PDMs bearing one or two deoxyhexose moieties that are further decorated with additional methyl groups in enriched probe-fed and control data sets. (b) MS/MS analysis of fucosylated ascr#3-LNK decorated with up to two methyl groups (36a–c, also Figures S15–S17). (c) EICs for m/z values corresponding to fucosas#10 (38) and derivatives with one or two additional methyl groups (fucosas#101 (39) and fucosas#102 (40), respectively) in acox-1.1, wildtype, and daf-22 exo-metabolomes. Fucosylated ascr#10 derivatives are observed in wild-type C. elegans, are more abundant in acox-1.1 mutants, and not detected in daf-22 mutant worms. Additional isomers of fucosylated ascr#10 derivatives represent fucosyl-ascarosides with shorter side chains and mono- and di-O-methylation of the fucose, as suggested by MS/MS analysis (Figures S18–S20). (d) EICs for fucosas#10 (38) in acox-1.1 exo-metabolome (black), a synthetic sample (green), and in a sample where synthetic fucosas#10 is added to acox-1.1 exo-metabolome (purple) confirm identification of fucosas#10. (e) Ascr#10 (34) and fucosas#10 (38) were quantified in the exo-metabolome of wildtype worms. Production of fucosas#10 is dependent on nutritional conditions, but not strongly dependent on life stage, unlike ascr#10.
