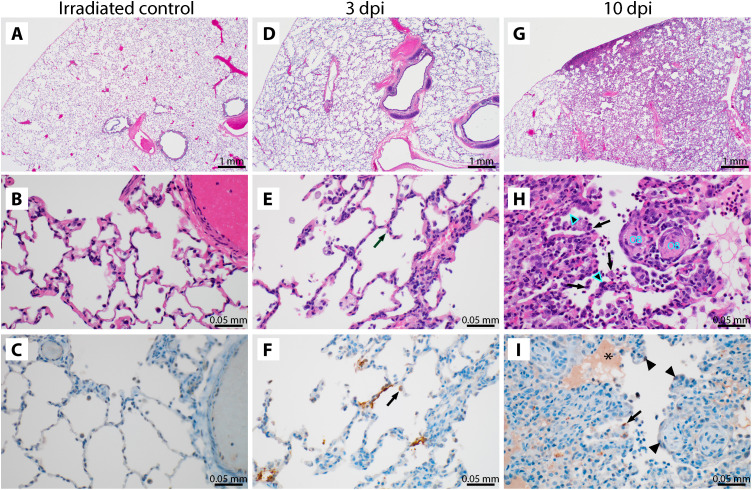
Fig. 2. Histological changes are observed in the lungs of African green monkeys inoculated with SARS-CoV-2.
(A to C) African green monkeys were inoculated with γ-irradiated SARS-CoV-2 (n = 2) and euthanized at 3 dpi; eight animals were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 isolate nCoV-WA1-2020. (D to F) Four of those were euthanized at 3 dpi. (G to I) The remaining four animals were euthanized at 10 dpi. Histological analysis was performed on lung tissue from all animals. (A) Lungs of animals inoculated with γ-irradiated SARS-CoV-2 were normal at 3 dpi. (B) This was further confirmed at high magnification. (C) No SARS-CoV-2 antigen could be detected in lungs from animals inoculated with γ-irradiated SARS-CoV-2. (D) Mildly thickened septa were observed at 3 dpi in animals inoculated with infectious SARS-CoV-2. (E) Alveolar septa are slightly thickened and more cellular at 3 dpi. (F) Cytoplasmic and membrane-associated viral antigen in pneumocytes at 3 dpi. (G) Discrete foci of interstitial pneumonia are apparent at the periphery of the lung at 10 dpi. (H) Alveolar edema (*), type II pneumocyte hyperplasia (arrowheads), increased alveolar macrophages (arrows), and infiltrating lymphocytes and neutrophils are observed at 10 dpi, as well as proliferative nodules associated with terminal airways resembling obstructive bronchiolitis (OB). (I) Rare viral antigen could be detected in mononuclear cells, presumably alveolar macrophages, with cytoplasmic debris (arrows) at 10 dpi; background blush is observed in alveolar proteinaceous fluid (*), but pneumocytes do not exhibit immunoreactivity (arrowheads). Magnification, ×20 (scale bars: 1 mm) (A to C) and ×400 (scale bars: 0.05 mm) (D to I).