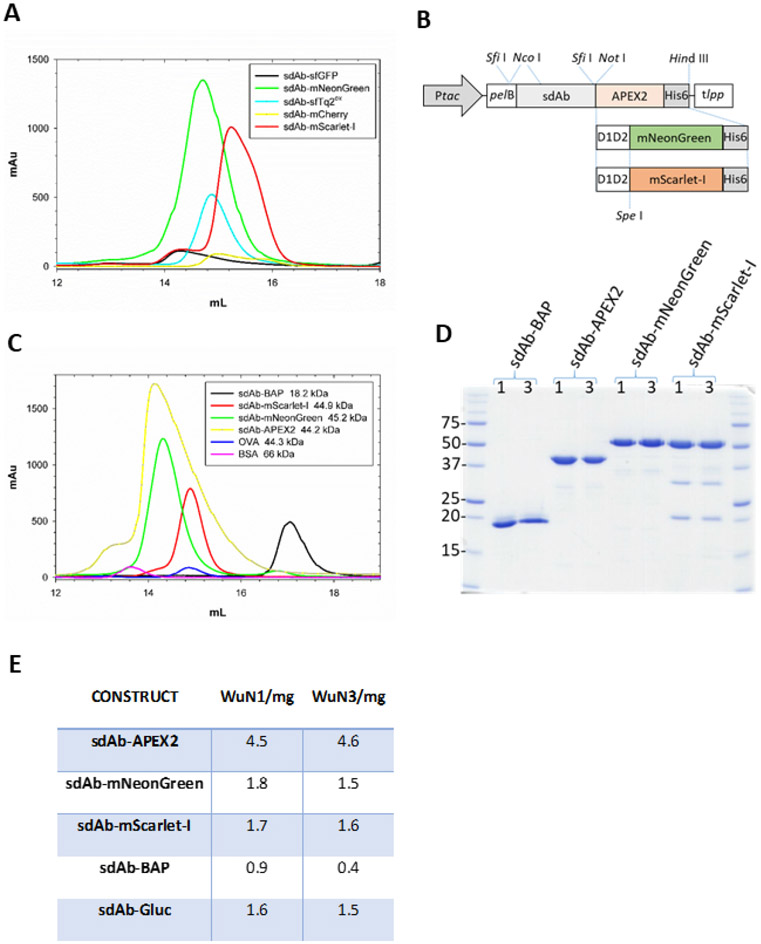
Figure 3.
Identification of fluorescent proteins capable of being overexpressed in the periplasm as sdAb fusions, their relative purity, and productivity. (A) Size exclusion chromatogram of the initial panel of FP fused to an anti-Marburgvirus NP sdAb following IMAC purification from the periplasmic compartment. sfGFP fusion (black), mNeonGreen fusion (green), sfTq2ox fusion (cyan), mCherry fusion (yellow) mScarlet-I (red). (B) Schematic of the E. coli periplasmic expression vector cassettes used to generate the anti-WuN sdAb fusion proteins used in the immunoprobing with the parental APEX2 gene being substituted for the D1D2-mNeonGreen and D1D2-mScarlet-I genes from the anti-Marburgvirus NP sdAb-FP fusions. Ptac, tac promoter; pelB, pectate lyase signal sequence; D1D2, M13 gene III linker; His6, polyhistidine tag; tlpp, terminator. (C) Size exclusion chromatograms of the sdAbWuN3 fusion proteins following IMAC purification from the periplasmic compartment. sdAb-BAP (black), APEX2 fusion (yellow), mNeonGreen fusion (green), mScarlet-I fusion (red), ovalbumin (OVA, blue), bovine serum albumin (BSA, pink). (D) Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of the purified proteins from both sdAbWuN1 and sdAbWuN3 fusion protein expressions. (E) Table of purified protein yields from one 500 mL expression culture for each of the main constructs.