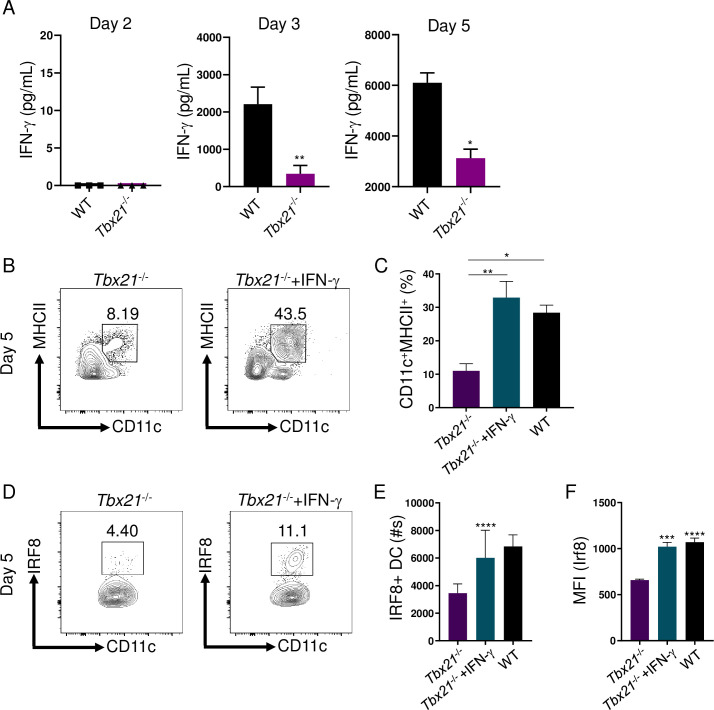
Fig 3. Early T-bet-dependent IFN-γ is critical to maintain inflammatory IRF8+ cDCs1.
(A) IFN-γ analysis by ELISA of serum in mice following T. gondii infection on days 2, 3, and 5 post-infection. (B-F) Tbx21-/- mice were i.p. infected with T. gondii and treated with or without IFN-γ. (B) Representative contour plots and (C) average frequencies of Lin-CD11c+MHCII+ DCs in the PECs were analyzed on day 5 following infection. (D) Representative contour plots and absolute quantification of (E) Lin-CD11c+MHCII+IRF8+ DCs in the PECs were analyzed on day 5 following infection. (F) Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of Lin-CD11c+MHCII+ DC IRF8 expression in the PECs was analyzed on day 5 post-infection. Results are representative of three-independent experiments involving at least 3 mice per group. Statistical analyses were done using (A, E, F) unpaired t-test analysis of individual groups or (C) one-way Anova with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. Error bars, standard error mean.