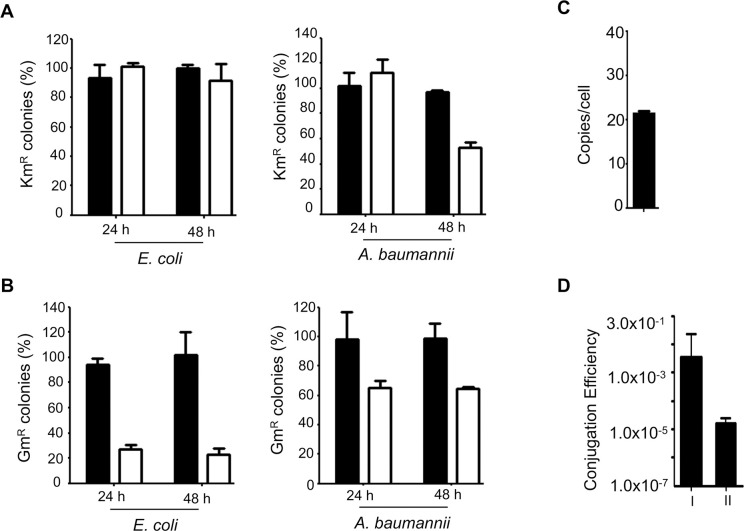
Fig 1. The stability of the IncQ plasmid pDSK519 in E. coli and A. baumannii.
A-B. Saturated cultures E. coli strain DH5a (left) and A. baumannii strain ATCC 17978 (right) harboring pDSK519 (A) or pVRL1 (B) were diluted 1:100 in fresh LB broth with (solid bars) or without (open bars) antibiotics and grown for 24 h and cells retaining the plasmid were determined. Data for the 48 h time point were obtained from further diluted cultures grown for an additional 24 h in LB broth without antibiotics. C. Plasmid copy number of pJL02 in A. baumannii. Plasmid copy number per cell was determined as described in Materials and Methods, and the results shown are average from three independent experiments each done in triplicate. Data shown were means ± SEM. D. Introduction of the IncQ plasmid pDSK519 into A. baumannii by conjugation. Cells from cultures of the donor, helper and the recipient strain (I) mixed at a 1:1:1 ratio were placed on nitrocellulose membranes for 4 h on LB plates. Transconjugants appeared on selective medium containing streptomycin and kanamycin were enumerated. The number of donor cells used for the experiments was similarly determined. For bi-parental conjugation, the donor strain and the recipient were mixt at 1:1 (II). In all cases, samples were done in triplicate and similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. Data shown were means ± SEM.