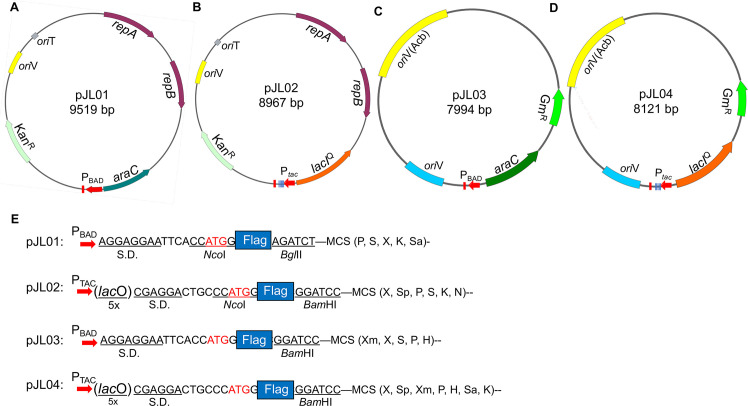
Fig 2. Diagrams of the four plasmids constructed in this study.
A-D. Important features of pJL01 (A), pJL02 (B), pJL03 (C) and pJL04 (D) are indicated on plasmid maps in distinct colors. The promoters PBAD and PTAC are indicated by red arrows at the bottom of each map. In each case, the red bar downstream of the promoter represents the T1T2 transcriptional terminators of the rrnB ribosomal gene. The five vertical bars downstream of the PTAC promoter in pJL02 and pJL04 represent the five copies of the lac operator. Other features such as antibiotic resistance genes and origins of replication are labeled on the maps. All maps were generated by the SnapGene software (GSL Biotech). E. The configuration of the elements for protein translation in the four plasmids. In each case, the sequence of the SD element, the space between the SD element and the translational start codon, the position of the Flag tag and the first restriction enzyme suitable for making Flag tagged fusions are indicated. Abbreviations for shown restriction enzymes: H, HindIII; K, KpnI; N, NotI; P, PstI; S, SacI; Sa, SalI; Sp, SpeI; X, XbaI; Xm, XmaI. Note the NcoI site immediately upstream of the sequence coding for the Flag tag in pJL01 and pJL02 that can be used to insert DNA fragments carrying alternative epitope tags. The information of additional restriction sites is available in the complete sequences of the plasmids.