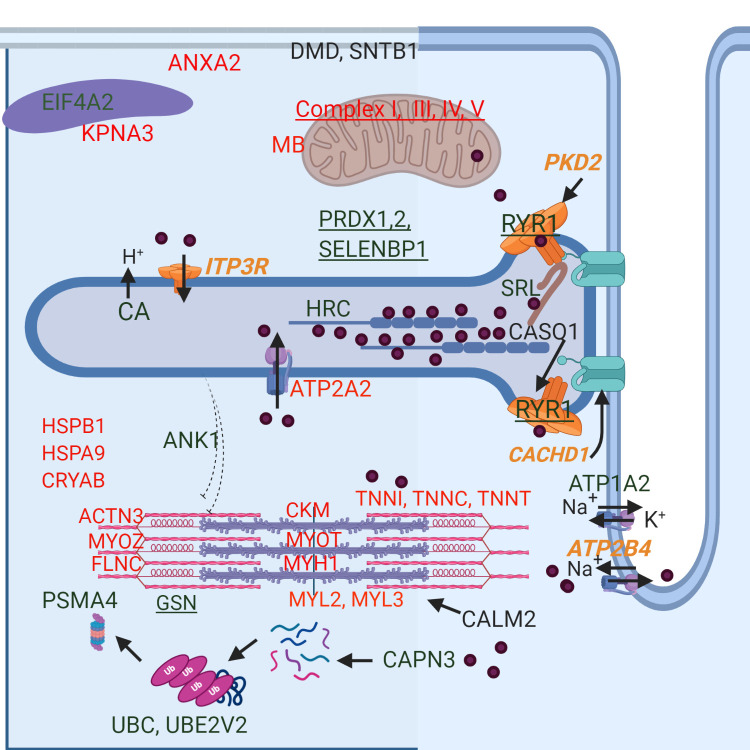
Fig 1. Depiction of the cellular location of differentially expressed proteins and select differentially expressed genes in RER-susceptible horses.
Increased expression is in green and decreased expression in red. Proteins that also had differential expression of their encoding gene are underlined. Differentially expressed genes (italics) relating to Ca2+regulation are shown in orange. Ca2+ is depicted by purple circles. Full names of genes and proteins are found in Tables 2–4. RER-susceptible horses between episodes of rhabdomyolysis had increased expression of ANK1, which links sarcoplasmic reticulum to myofilaments, Ca2+ binding proteins within the sarcoplasmic reticulum (CASQ1, SRL, HRC), the Ca2+ release channels ITP3R and RYR1, as well as regulators of RYR1 [calmodulin (CALM2), calsequestrin (CASQ1), PKD2, and CACHD1 (via DHPR)]. Proteins involved in oxidative stress (PRDX1, PRDX2, SELENBP1) and protein degradation [Ca2+-activated calpain (CAPN3), ubiquitination (UBC, UBE2V2), proteasome (PSMA4)] were differentially expressed. Decreased expression was found for Ca2+ activated proteins [SERCA2 (ATP2A2), troponins (TNN1,C,T) myosin regulatory light chains (MYL2,3)] as well as other sarcomere proteins (ACTN3, MYOZ, FLNC, MYH1). Heat shock proteins (HSPB1, HSPA9) and protein chaperones had decreased expression in RER. Decreased expression was found for mitochondrial proteins myoglobin (MB), 6 subunits of complex I, 3 subunits of complex III, 4 subunits of complex IV and 4 subunits of complex V. ANXA2, a Ca2+ activated membrane repair protein was also downregulated and sarcolemmal structural proteins dystrophin (DMD) and syntrophin (SNTB1) were upregulated. The sodium/potassium exchanger (ATP1A2) and the sodium/ Ca2+ exchanger ATP2B4, were also differentially expressed.