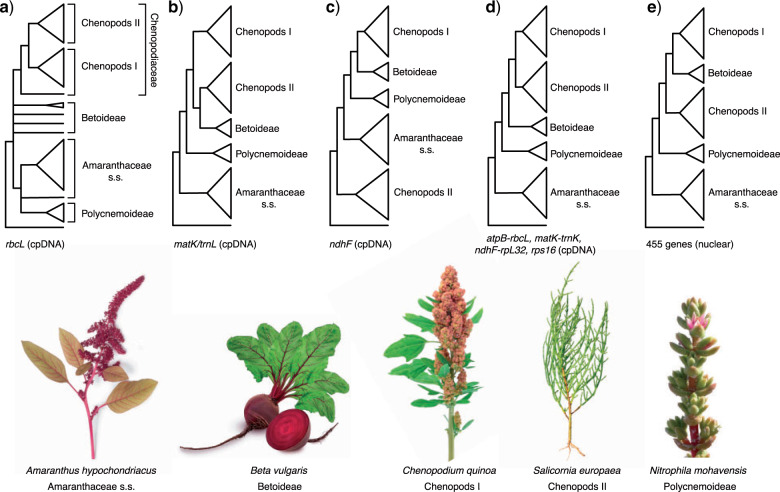
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic hypotheses of Amaranthaceae s.l. from previous studies. a) Kadereit et al. (2003) using the plastid (cpDNA) rbcL coding region. b) Müller and Borsch (2005); using the cpDNA matK coding region and partial trnL intron. c) Hohmann et al. (2006) using the cpDNA ndhF coding region d) Kadereit et al. (2017) using the cpDNA atpB-rbcL spacer, matK with trnL intron, ndhF-rpL32 spacer, and rps16 intron. e) Walker et al. (2018) using 455 nuclear genes from transcriptome data. Major clades of Amaranthaceae s.l. named following the results of this study. Image credits: Amaranthus hypochondriacus by Picture Partners, Beta vulgaris by Olha Huchek, Chenopodium quinoa by Diana Mower, Nitrophila mohavensis by James M. André, and Salicornia europaea by Homeydesign.