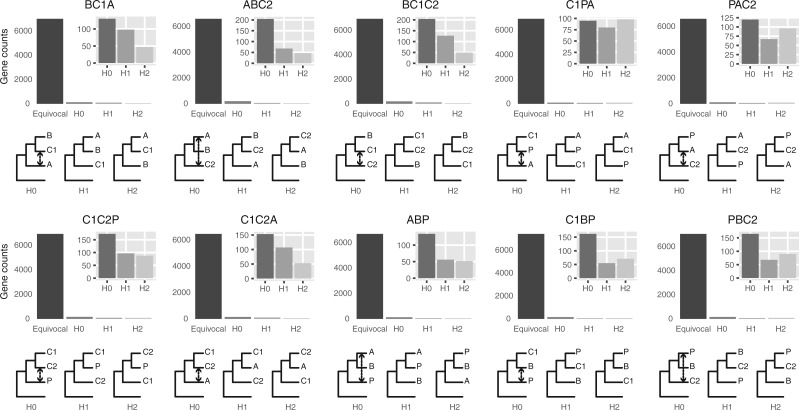
Figure 4.
Gene counts from approximate unbiased (AU) topology test of the 10 quartets from the five main clades of Amaranthaceae s.l. AU tests were carried out between the three possible topologies of each quartet. H0 represents the ASTRAL species tree of each quartet. ``Equivocal'' indicates gene trees that fail to reject all three alternative topologies for a quartet with 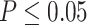 . Gene counts for each of the three alternative topologies represent gene trees supporting unequivocally one topology by rejecting the other two alternatives with
. Gene counts for each of the three alternative topologies represent gene trees supporting unequivocally one topology by rejecting the other two alternatives with 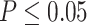 . Insets represent gene counts only for unequivocal topology support. Double arrowed lines in each H0 quartet represent the direction of introgression from the ABBA/BABA test. Each quartet is named following the species tree topology, where the first two species are sister to each other. A
. Insets represent gene counts only for unequivocal topology support. Double arrowed lines in each H0 quartet represent the direction of introgression from the ABBA/BABA test. Each quartet is named following the species tree topology, where the first two species are sister to each other. A  Amaranthaceae s.s. (represented by Amaranthus hypochondriacus), B
Amaranthaceae s.s. (represented by Amaranthus hypochondriacus), B  Betoideae (Beta vulgaris), C1
Betoideae (Beta vulgaris), C1  Chenopods I (Chenopodium quinoa), C2
Chenopods I (Chenopodium quinoa), C2  Chenopods II (Caroxylon vermiculatum), P
Chenopods II (Caroxylon vermiculatum), P  Polycnemoideae (Polycnemum majus). All quartets are rooted with Mesembryanthemum crystallinum.
Polycnemoideae (Polycnemum majus). All quartets are rooted with Mesembryanthemum crystallinum.