Figure 1.
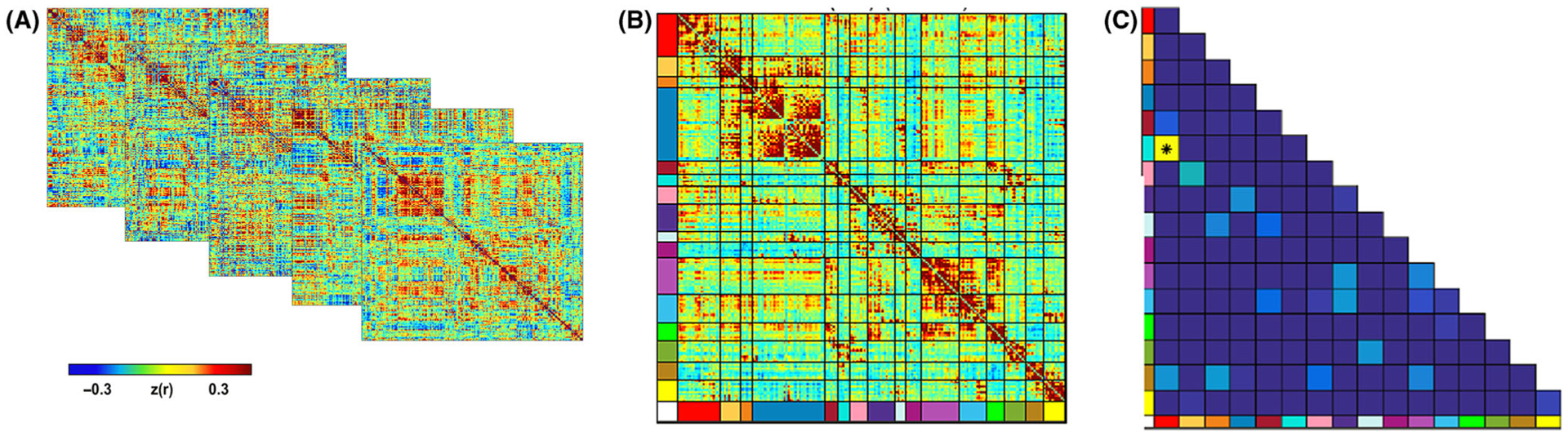
Overview of fetal fMRI statistical approach. Pearson correlation matrices (panel A) reflecting 197 ROIs for each participant were analyzed to create a subnetwork model of the fetal brain. The complete set of unique n = 19,306 ROI pair functional connectivity (Fisher-z) values from all participants were then averaged, producing a 197 × 197 connectivity matrix (panel B). In order to test the effects of maternal BMI at the network-pair level, enrichment analysis was then performed to identify individual ROI pairs with functional connectivity related to maternal prenatal BMI. Subsequently Chi-squared statistic was used to determine whether the number of significant ROI pairs (p < .05) within a network pair was greater than expected by chance (panel C). This approach was developed by Eggebrecht et al. (2017).
