Fig. 2. Abnormal neuronal activation and synaptic transmission in F0 males of depression-like model is conferred to offspring.
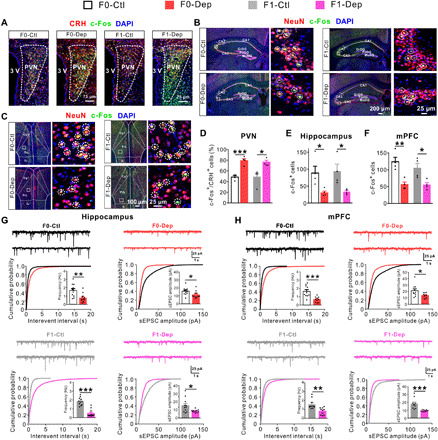
(A and D) Triple immunostaining for CRH (red), c-Fos (green), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) showing the activation of CRH neurons in the PVN of F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl and F1-Dep versus F1-Ctl under baseline conditions (n = 4). (B and E) Triple immunostaining for NeuN (red), c-Fos (green), and DAPI (blue) showing the neuronal activation in the hippocampus of F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl and F1-Dep versus F1-Ctl under baseline conditions (n = 4). Circles indicate the activated neurons. GrDG, granular layer of the dentate gyrus; PoDG, polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus; MoDG, molecular layer of the dentate gyrus. (C and F) Neuronal activation in the mPFC of F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl and F1-Dep versus F1-Ctl under baseline conditions (n = 4). Circles indicate the activated neurons. PrL, prelimbic; Cg1, cingulate cortex, area 1; IL, infralimbic cortex. (G) Raw current traces showing sEPSCs recorded in the hippocampal pyramidal neurons, and the cumulative distribution of sEPSC interevent interval and amplitude with the average frequency and amplitude (insets) of F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl and F1-Dep versus F1-Ctl under baseline conditions (n = 11 to 12 neurons from five mice per group). (H) Frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs in the mPFC pyramidal neurons of F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl and F1-Dep versus F1-Ctl under baseline conditions (n = 10 neurons from five mice per group).
