Fig. 4. Adjusting the imbalance of miRNAs in zygotes can rescue the abnormalities in the F1 offspring born to F0 males of depression-like model.
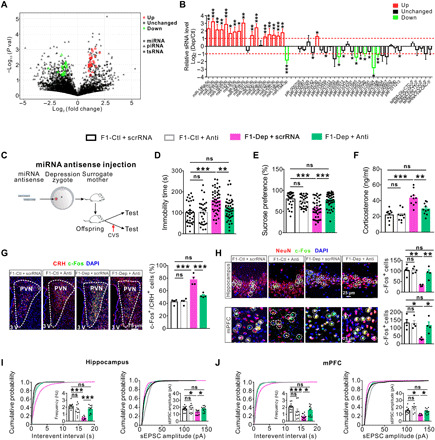
(A) Scatter plot comparison illustrating sperm sRNAs that were differentially expressed between F0-Dep and F0-Ctl (n = 3). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the expression of sperm sRNAs in F0-Dep versus F0-Ctl (n = 10). (C) Schematic timeline and behavioral paradigm in IVF offspring born to zygotes injected with miRNA antisense strands (F1-Dep + Anti or F1-Ctl + Anti) or with scrRNA (F1-Dep + scrRNA or F1-Ctl + scrRNA). (D and E) Behavioral performances in FST (n = 30 to 47) and SPT (n = 30 to 47) after exposure to CVS. (F) Plasma corticosterone levels in F1-Dep + Anti, F1-Ctl + Anti, F1-Dep + scrRNA, and F1-Ctl + scrRNA under baseline conditions (n = 10). (G) Activation of CRH neurons in the PVN of F1-Dep + Anti, F1-Ctl + Anti, F1-Dep + scrRNA, and F1-Ctl + scrRNA under baseline conditions (n = 4). (H) Neuronal activation in the hippocampus and mPFC of F1-Dep + Anti, F1-Ctl + Anti, F1-Dep + scrRNA, and F1-Ctl + scrRNA under baseline conditions (n = 4). (I and J) Frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs in the hippocampal and mPFC pyramidal neurons of F1-Dep + Anti, F1-Ctl + Anti, F1-Dep + scrRNA, and F1-Ctl + scrRNA under baseline conditions (n = 9 to 15 neurons from five mice per group).
