Fig. 2. DNA methylation analysis on tumor-specific lincRNAs revealed EPIC1 as a suppressor of tumor immune response.
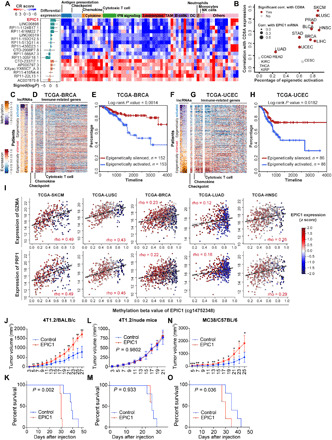
(A) Consensus regulation (CR) score of 11 EA tumor-specific lincRNAs (C2 cluster) and 6 epigenetically silenced (ES) tumor-specific lincRNAs (C4 cluster) that are correlated with tumor immune response (heatmap) and their average differential expression across 23 cancer types (bar plots). (B) Correlation between epigenetic activation fraction of epigenetically induced lincRNA 1 (EPIC1) and its association with CD8A expression. (C, D, F, and G) DNA methylation (z score normalized beta value) of tumor-specific lincRNAs (C and F) and the expression of immune signature genes (D and G) in TCGA-BRCA and TCGA-UCEC patients. BRCA, Breast Cancer; UCEC, Uterine Corpus. (E and H) Survival curves of the patients with top and bottom 20% epigenetic activity in (C) and (F). (I) Correlation between EPIC1 methylation and GZMA and PRF1 expression. (J to O) Tumor volume (J, L, and N) and overall survival (K, M, and O) of BALB/c mice, BALB/c nude mice, and C57BL/6 mice that are inoculated with 4T1.2 cells or MC38 cells stably expressing empty vector (control) or EPIC1 (n = 5 animals per group). EC, Endometrial Carcinoma; GZMA, Granzyme A; PRF1, Perforin 1. Data are means ±SD. *P <0.05; **P <0.01; ***P < 0.001.
