Fig. 6. EPIC1’s regulation of type II interferon signaling is mediated by its interaction with EZH2 protein.
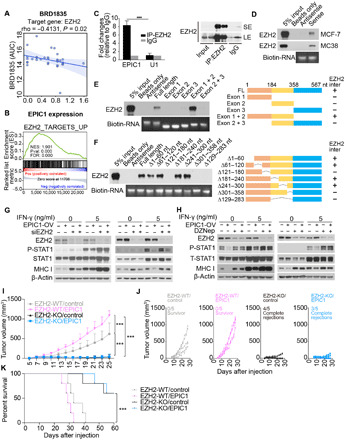
(A) Correlation between EPIC1 expression and PRC2 inhibitor response in breast cancer cell lines. (B) Gene set enrichment analysis of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) targets in siEPIC1-treated MCF-7 cell lines. (C) The enrichment of EPIC1 and U1 by EZH2 RNA immunoprecipitation assay analyzed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Immunoblot of EZH2 indicates the immunoprecipitation efficiency of EZH2 (right). LS, long exposure; SE, short exposure. (D) Immunoblot of EZH2 protein retrieved by in vitro transcribed EPIC1 from MCF-7 and MC38 cells’ nuclear extracts. (E and F) Immunoblot of EZH2 pulled down by indicated EPIC1 truncations (E) and deletions (F). The right panels are the schematic of indicated EPIC1 deletions and their binding with EZH2 (i.e., EZH2-inter). (G and H) Measurement of p-STAT and MHC-I protein levels by immunoblot in MCF-7 (left) and HCT116 (right) stable cell line overexpressing EPIC1 and rescued with EZH2 siRNA treatment (G) or EZH2 inhibitor DZNep treatment (H). (I and J) Tumor size of EZH2 wild-type (WT) or knocked out (KO) 4T1.2 cells stably expressed by empty vector (control) and EPIC1 (n = 5 animals per group). Tumor size was measured every other day. ***P < 0.001. (K) Survival curve for each group in (I).
