Fig. 1. kor1 mutant roots display increased JA-Ile levels and signaling.
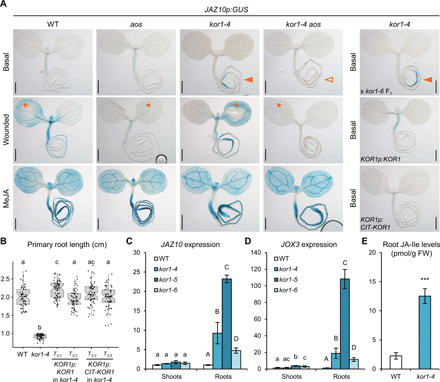
(A) Representative JAZ10p:GUS (JGP) reporter activity in 5-do seedlings of WT, aos, kor1-4, kor1-4 aos at basal conditions, 2 hours after cotyledon wounding (orange asterisks), 2 hours after 25 μM MeJA treatment, and in kor1-4 x kor1-6 F1 (allelism test), kor1-4 complemented with KOR1p:KOR1 and KOR1p:CIT-KOR1 lines. Note the increased JAZ10p:GUS reporter activity in kor1-4 and allelism test (orange arrowheads) and its absence from kor1-4 aos (empty arrowhead). Scale bars, 0.5 mm. (B) Primary root length box plot summary in 7-do WT, kor1-4, and two independent T3 lines for each complementing KOR1p:KOR1 and KOR1p:CIT-KOR1 construct. Both constructs restored the kor1-4 short root phenotype to WT length. Medians are represented inside the boxes by solid lines, and circles depict individual measurements (n = 59 to 61). (C and D) Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of basal (C) JAZ10 and (D) JOX3 expression in shoots and roots of WT and three kor1 mutant alleles. JAZ10 and JOX3 transcript levels were normalized to those of UBC21. Bars represent the means of three biological replicates (±SD), each containing a pool of ~60 organs from 5-do seedlings. (E) Absolute JA-Ile content in WT and kor1-4 roots. Bars represent the means of three biological replicates (±SD), each containing a pool of ~600 roots from 5-do seedlings. Letters and asterisks denote statistically significant differences among samples as determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s honest significant difference (HSD) test (P < 0.05) in (B) to (D) and by Student’s t test (P = 0.0005) in (E).
