Figure 3.
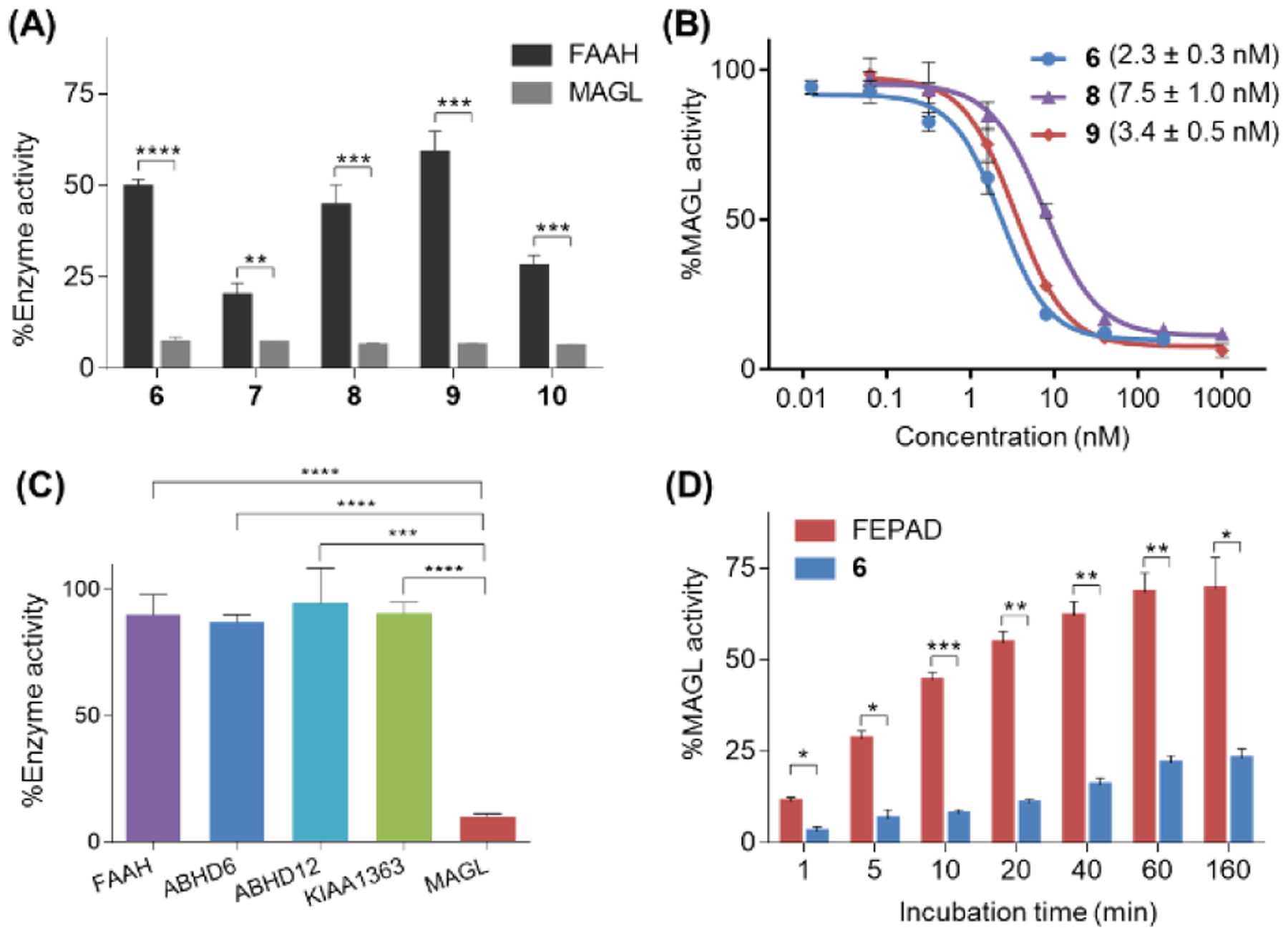
Inhibition properties of MAGL activity by compounds 6–10 determined by ABPP assay. (A) Inhibition of mouse brain MAGL and FAAH activity with compounds 6-10 (5 μM); (B) Concentration-response curves of 6, 8 and 9 for inhibition of mouse brain MAGL; (C) Subtype selectivity of 6 (at 200 nM) among MAGL and other serine hydrolases in the endocannabinoid system including KIAA1363, FAAH, ABHD6 and ABHD12; (D) MAGL activity determined at different time points with 6 (at 200 nM). A reversible inhibitor FEPAD (at 1 μM) was used as a control. No significant time-dependent changes of MAGL activity indicates that the binding of compound 6 is irreversible while the reversible inhibitor FEPAD exhibits recovered MAGL activity over time. All data are mean ± SD, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p ≤0.01, and ***p ≤0.001.
