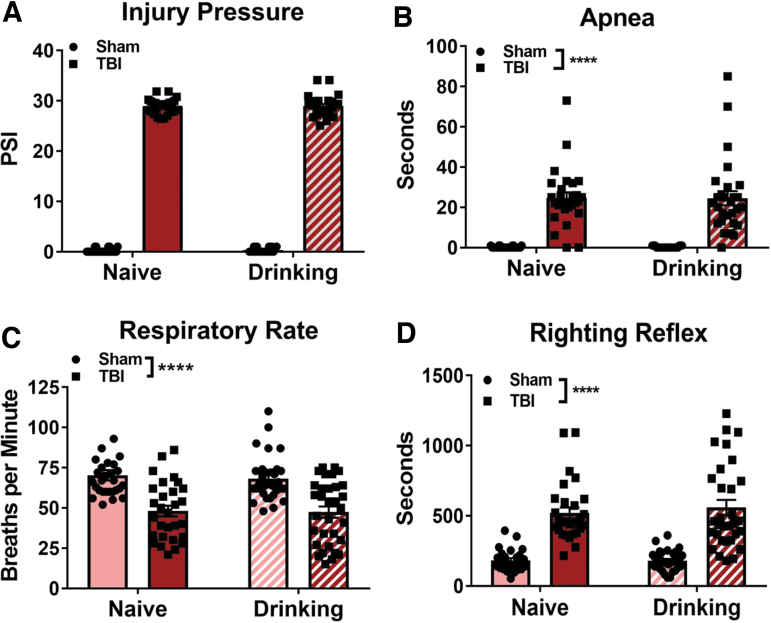
FIG. 1.
Alcohol self-administration does not alter measures of TBI severity in female rats. Alcohol-naïve and alcohol-drinking TBI animals received equivalent injury pressures (A). Immediately post-TBI, alcohol-naïve and alcohol-drinking animals showed similar lengths of apnea (B), decreases in respiratory rate (C), and latency to righting reflex (D) relative to uninjured Shams. Injury pressures were compared with two-tailed unpaired t test. Other data were analyzed via two-way ANOVA, ****p < 0.0001 main effect of TBI, n = 28–35/group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ANOVA, analysis of variance; SEM, standard error of the mean; TBI, traumatic brain injury.