FIGURE 6.
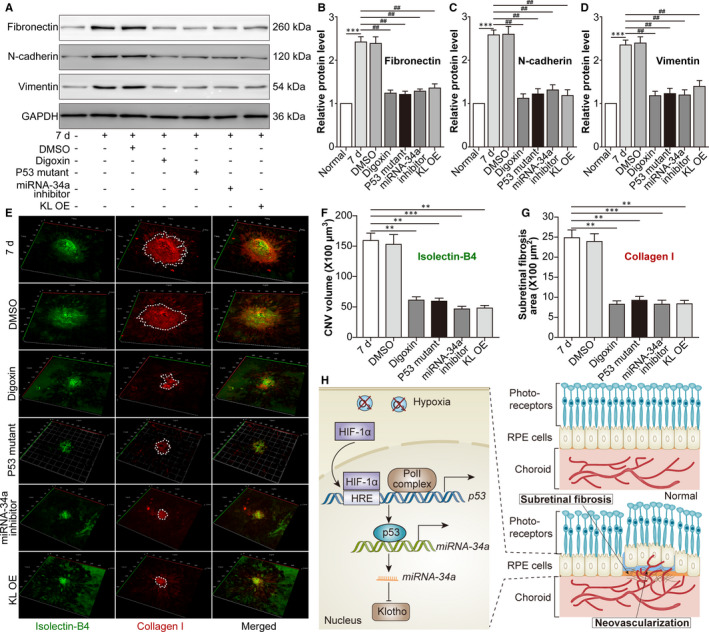
Blockade of the HIF‐1α/p53/miRNA‐34a axis mitigates subretinal fibrosis in a mouse CNV‐induced CNV model. The mice were divided into the following groups: normal, CNV 7 d, CNV 7 d + 0.1% DMSO, CNV 7 d + digoxin, CNV 7 d + AAV‐p53 mutant, CNV 7 d + miRNA 34a inhibitor and CNV 7 d + AAV‐Klotho full‐length plasmid. A, Western blot was performed to measure Fib, N‐cad and Vim protein levels in retina‐RPE‐choroid tissues. *** P < .001, CNV 7‐d group vs normal group. ## P < .01, compared with the CNV 7‐d group. B, Relative protein levels of Fib (B), N‐cad (C) and Vim (D) compared with GAPDH levels were analysed. E, IB4 (green) and type I collagen (colI; red) were stained on the choroidal flat mount. F, The volume of CNV was analysed. G, The subretinal fibrosis area was analysed. ** P < .01, *** P < .001, compared with the CNV 7‐d group in Figure 6F,G. H, A schematic diagram displaying the role of HIF‐1α/p53/miRNA‐34a in CNV is shown. Under hypoxic conditions, HIF‐1α up‐regulates p53 activation, increases miRNA‐34a, down‐regulates Klotho and promotes EMT in RPE cells, facilitating subretinal fibrosis and the progression of CNV. Moreover, blockade of the HIF‐1α/p53/miRNA‐34a axis alleviates subretinal fibrosis and the formation of CNV
